Top 12 Software Development Methodologies
 Admin
Admin Software Development
Software Development Apr 09, 2024
Apr 09, 2024

Table of Content
Every software team wants to deliver faster, with fewer bugs and less confusion. But how you get there depends on how your team works. That is where development methodologies play a key role.
Agile, Waterfall, DevOps, RAD — each one is designed to solve a specific type of challenge. Some focus on speed and flexibility. Others offer structure and predictability. The real challenge is not learning every method but understanding when to apply the right one.
In this article, we explain the most common software development methodologies, their advantages, limitations, and real-world use cases. Whether you're working on a custom platform, a mobile app, or an enterprise system, this guide will help you understand which method suits your project's scope, timeline, and flexibility requirements.
What is Software Development Methodology?
Software development methodology is a set of guidelines that helps teams plan, build, test, and deliver successful software. Each methodology has steps and practices that guide the development process from start to finish.
The choice of methodology can affect the result of your software project. It influences how your team works together, how fast they develop software, and how well it meets users' needs. Thus, a software development methodology organizes the complex software development process. It makes the development process more predictable and manageable.
Top Software Development Methodologies
Custom software development services are tailor-made software solutions that cater specifically to the needs of a business. The choice of development methodology plays a critical role here, as it affects everything from requirement gathering to deployment, aligning the development process with the unique demands of custom solutions.
Let's explore the top software development methodologies that help you in simplifying custom software development process .
1. Agile Methodology
Agile is a flexible development methodology that emphasizes iterative progress, collaboration, and customer feedback. Its key features include sprints, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives, facilitating rapid adjustments and continuous improvement.

Advantages
High-Quality Output
Continuous testing and fine-tuning lead to minimal software defects.
Clear Communication
Frequent and transparent interactions promote better teamwork and alignment with business stakeholders.
Flexibility
Your team can make changes to project requirements with minimal impact on timelines, delivering value to users.
Customer Satisfaction
Rapid and continuous software delivery increases your business's efficiency to meet customers' needs.
Human Interaction
The agile method enables direct communication and constant feedback from customer representatives. You can align the product better with customer expectations.
Adaptive Approach
Agile’s flexibility allows it to respond swiftly to changing client requirements.
Disadvantages
Focus Challenges
Teams can lose focus when overwhelmed with frequent change requests.
Limited Documentation
Agile's emphasis on working with software over documentation leads to knowledge sharing. Thus, regulatory compliance challenges may arise.
Time-Consuming Feedback
Discussions and feedback, while essential, can consume a significant amount of time.
Discipline and Engagement
You need to ensure high levels of discipline and engagement to avoid communication overheads.
Complex Estimations
Assessing the project deadline can be challenging due to frequent changes and short sprints.
Use case
Many leading tech companies have adopted Agile to speed up their development processes and improve product quality. A notable example is Spotify, which has effectively implemented Agile principles to enhance its team's productivity and collaboration.
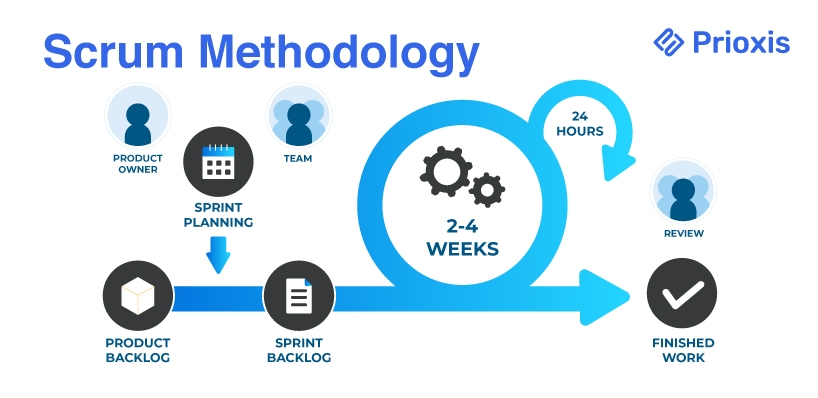
2. Scrum Methodology
Scrum, a subset of Agile, organizes work in fixed-length iterations called sprints. Key roles include the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, each contributing to the project's success through clearly defined responsibilities.
Benefits
Quick Problem Resolution
Short iterations enable fast identification and resolution of problems.
High Responsiveness
Regular feedback and adaptability ensure that the development process is responsive to changes.
Cost-Effective
Scrum is cost-efficient and proves to be an effective methodology for many projects.
Enhanced Team Alignment
Regular meetings keep all team members informed and aligned, fostering better collaboration.
Recognition of Contributions
Individual team members' contributions are highlighted and appreciated through Scrum meetings.
Decision-Making Autonomy
Teams have complete control over decision-making, promoting empowerment and accountability.
Frequent Progress Updates
Constant updates and feedback help maintain the project's direction, quality, and timely delivery.
Disadvantages
Skill and Commitment Requirements
All team members must be skilled and committed for Scrum to be successful.
Potential for Burnout
Daily Scrum meetings can be exhausting and may lead to team burnout.
Challenges with Large Projects
Scrum’s focus on close collaboration and frequent communication may not be suitable for large projects.
Scope Creep
The flexibility of Scrum can lead to scope creep, making it difficult to define an end date.
Strict Control Issues
The Scrum Master's strict control can lead to frustration and demoralization among team members. There is a possibility of project failure due to this.
Use case
Companies like Google and IBM use Scrum to manage complex software development projects, benefiting from its structured yet flexible approach to project management.
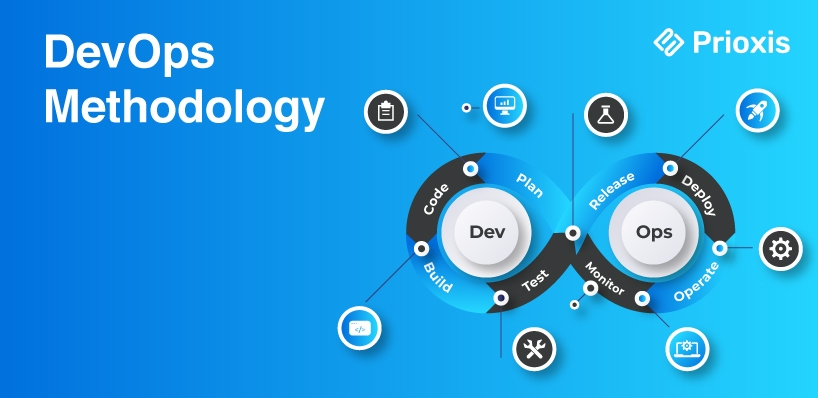
3. DevOps Methodology
DevOps bridges the gap between development and operations, focusing on continuous integration, delivery, and deployment. Its core principles include automation, monitoring, and collaboration, aiming to streamline the software deployment process.
Advantages
Faster Processes
DevOps enables the simultaneous running of many processes. It accelerates workflows and enables businesses to adapt to market changes, driving efficient growth and business outcomes.
Rapid Deliveries:
With microservices and continuous delivery, DevOps ensures business continuity and rapid updates.
Reliability
Frequent updates make the developed products robust, secure, and competitive.
Collaboration
DevOps promotes a collaborative environment with strong accountability and ownership. It also aligns development and operations teams for faster and more effective product delivery.
Improved Time to Market
DevOps automates continuous deployment. As a result, your time to market decreases. While customer satisfaction and product quality increase. Plus, employee productivity rises.
Disadvantages
Cultural Change
Implementing DevOps lifecycles requires a significant cultural shift and a restart of processes to align with the new methodology.
Organizational Upgradation
You must upgrade from traditional methods to a multidisciplinary approach.
Regulatory Constraints
Certain industries need extensive testing before moving projects to the operations phase, which can conflict with DevOps practices.
Environmental Inconsistencies
If different departments use different environments, undetected issues may slip into production.
Need for Human Interaction
Some quality attributes still require human oversight, slowing down the delivery pipeline.
Use case
Amazon Web Services (AWS) exemplifies the successful implementation of DevOps, showcasing significant improvements in deployment methods, frequency and operational stability.
When planning to implement DevOps methodology in your development process, it is crucial to hire the best DevOps engineers. Hiring qualified DevOps engineers will resolve many of the implementation challenges.
4. Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model is a linear and sequential approach, where each phase must be completed before the next begins. Stages include requirement gathering, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance.

Advantages
Simplicity and Clarity
The waterfall model's linear nature makes it easy to understand and manage, especially for beginners.
Well-Defined Specifications
You must outline requirements and deliverables upfront, ensuring clear expectations before development begins.
Effective for Smaller Projects
The Waterfall model works well for projects with well-defined requirements and limited scope.
Structured Phases
Each phase has defined deliverables and a review process, making project management easy.
Time Efficiency
The model can save time since all phases are processed and completed sequentially.
Disadvantages
Lack of Early Feedback
Customer feedback is not incorporated in the early phases, which increases the risk of the project veering off target.
Late Testing
Testing is performed only at the end of the development process, making it more difficult to fix problems.
Rigidity
The Waterfall model does not accommodate mid-project adjustments. Thus, making it unsuitable for complex or evolving projects.
Overemphasis on Documentation
Excessive focus on documentation can detract from delivering effective solutions.
Use case
The Waterfall model is best suited for projects with well-defined needs and where changes are unlikely. It's ideal for development teams that prefer a structured and predictable workflow.
5. Prototype Methodology

This methodology involves creating a working model of the software product early in the development process. It allows for early feedback and adjustments, significantly improving the final product's alignment with user expectations.
Advantages
Enhanced Customer Understanding
Prototypes give a tangible feel of the software’s functionality. Based on the prototype, you can ensure higher customer satisfaction and comfort.
Scope for Refinement
Early prototypes help identify improvement areas, allowing new changes to be accommodated effectively.
Reduced Risk
Early identification of potential risks and issues reduces the likelihood of project failure with timely corrective measures.
Efficient Need Gathering
Prototypes are useful for gathering and analyzing requirements, especially when lacking documentation.
Disadvantages
Cost Implications
Prototyping can be expensive for developers. Also, the excessive use of resources can inflate the organization’s development costs.
Client Involvement
Over-involvement of clients may not always align with the developers' workflow and priorities.
Customer Dissatisfaction
Clients may become dissatisfied or lose interest if the initial prototype does not meet their expectations.
Use case
Dropbox is a prime example, initially launching a simple video prototype to demonstrate its concept, which significantly influenced its product development strategy based on user feedback.
You might be confused about several similar terminology like prototype, POC or MVP. This article can help you clear all doubts.
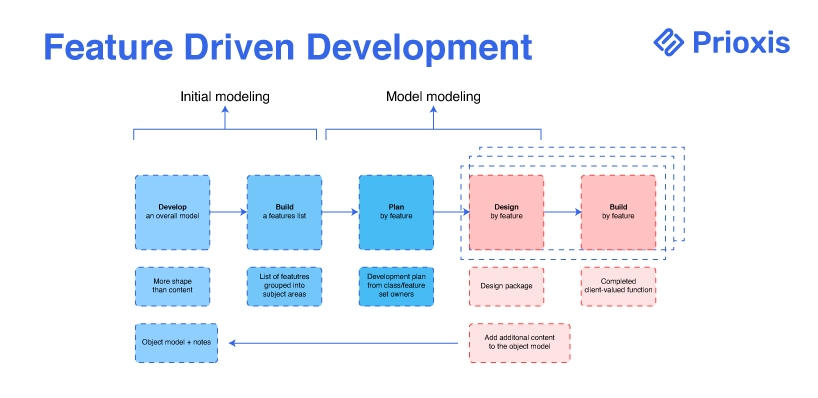
6. Feature Driven Development
Feature Driven Development (FDD) focuses on delivering tangible, working software repeatedly in a timely manner. It emphasizes feature value, domain object modeling, and regular builds to ensure quick, consistent progress.
Advantages
Efficient Task Management
Breaks down complicated tasks into smaller activities, enhancing efficiency and manageability.
Simultaneous Task Handling
Large teams can work on many tasks, increasing productivity and reducing project timelines.
Progress Tracking
Provides a clear and focused development path with a feature-based approach for progress tracking.
Industry Standards
Depends on predefined standards and best practices, leading to predictable and high-quality outcomes.
Effective for Large Projects
Well-suited for large projects, ensuring repeatable success through its structured approach.
Disadvantages
Complex for Small Projects
Not ideal for smaller projects where its structured approach may be complex and unmanageable.
Dependency on Lead Developer
Dependent on the lead developer for task coordination, which can create bottlenecks and impact project flow.
Lack of Documentation
Provides minimal written documentation to clients, which can be a drawback for proof of progress.
Activity-Driven Focus
It may sometimes focus on activities that over-deliver user value, as the model is driven by tasks rather than end-user benefits.
Use case
Large financial institutions often employ FDD to manage their complex software development needs, benefiting from its structured approach to managing extensive projects and teams.
7. Rapid Application Development (RAD)
RAD is a type of Agile methodology that prioritizes rapid prototyping over lengthy planning phases. The focus is on quickly developing a high-quality software product through iterative development and feedback loops.

Advantages
Reduced Risk
Regular customer feedback throughout the development process helps identify and mitigate risks early.
Increased Customer Satisfaction
Constant engagement and iterative improvements lead to higher customer satisfaction.
Suitability for Small to Medium Applications
Works well for small and medium-sized applications, ensuring quick development and delivery.
Quick Time-to-Market
Streamlined development processes reduce the time-to-market.
Prototyping Benefits
RAD's prototyping nature allows for quick reviews and fewer defects. Thus, clients receive high-priority functionality at each phase.
Disadvantages
Dependence on Responsive Customers
Requires responsive customers for continual feedback, which may not always be available.
High Costs
It is not suitable for projects with low budget constraints. Due to the potential high costs associated with modeling and automated code generation.
Lack of Documentation
Insufficient documentation for effective progress tracking, which can impact project management.
Limited to Modular Systems
Only works well for systems that can be modularized, limiting its applicability for some projects.
Use cases
Companies like Facebook have utilized RAD principles, enabling them to launch new features rapidly and refine them based on real-time user feedback.
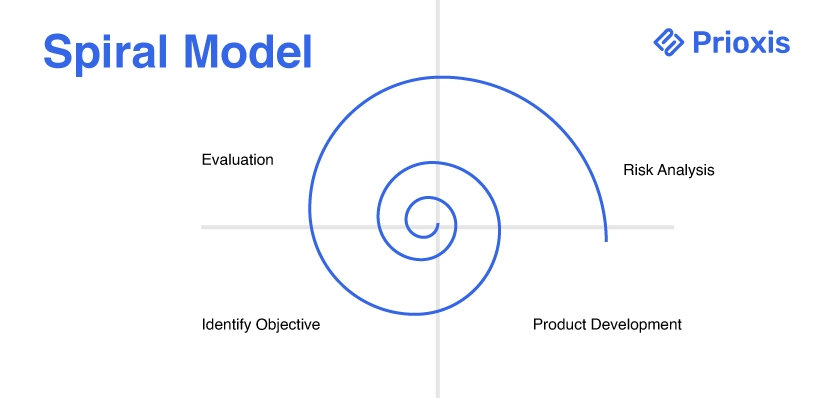
8. Spiral Model
The Spiral Model combines iterative development with the systematic aspects of the Waterfall model, emphasizing risk analysis at each phase. This model allows for incremental releases of the product, facilitating early detection and mitigation of risks.
Advantages
Extensive Risk Analysis
The extensive risk analysis reduces the likelihood of potential risks. If your project involves high-risk projects this model is appropriate.
Ideal for Large and Critical Projects
Particularly well-suited for large, complex, and mission-critical projects.
Flexibility for Extra Functionality
Allows for adding new features and functionality at later stages of development.
Rapid and Systematic Development
Development is fast and features are systematically added, ensuring steady progress.
Adaptability to Changing Business Needs
Better suited for projects where business requirements may frequently change.
Disadvantages
High Development Costs
The model can be costly due to extensive risk analysis and iterative processes.
Dependency on Risk Analysis
The project's success relies on the risk analysis phase; failure in this phase can jeopardize the entire project.
Not Suitable for Low-Risk Projects
The spiral model is inappropriate for low-risk projects, as it can be complex and resource-intensive.
Extensive Documentation
Requires more documentation due to its intermediate phases, which can be time-consuming and cumbersome.
Use Case
Aerospace and defense projects often utilize the Spiral Model to handle the high level of complexity and risk management required in such endeavors.
9. Dynamic Systems Development Model Methodology
The Dynamic Systems Development Model (DSDM) is an Agile framework that focuses on delivering software projects in a timely and cost-efficient manner. It emphasizes stakeholder involvement, project delivery in frequent increments, and the ability to adapt to changing requirements.

Advantages
Prompt Delivery of Basic Functionalities
The iterative approach ensures that essential software functions are delivered quickly. It also ensures that additional features are added at regular intervals.
Enhanced Control
Developers have better control over the development timeline and budget. Thus, projects are completed on time and within budget.
Comprehensive Documentation
Necessary documentation is created throughout development, facilitating better tracking and communication.
Strong Communication
Establishes effective communication between end-users and developers. Plus, it also keeps the team aligned with project goals.
User Involvement
High user involvement in the development process increases the likelihood of meeting user needs and expectations.
Disadvantages
High Implementation Costs
Implementing DSDM can be expensive due to the need for extensive user and developer involvement and significant training expenses.
Complexity
The concept and implementation of DSDM are complex, posing challenges in adoption and execution, particularly for smaller teams.
Unsuitable for Small Organizations
Due to its cost and complexity, this methodology may not be suitable for small organizations or one-time projects.
Limited Developer Creativity
The focus on adhering to documentation and standards can limit the scope for developer creativity and innovation.
Use Case
Telecommunication companies undergoing constant evolution in technologies and customer demands have successfully applied DSDM to keep pace with industry advancements while delivering high-quality software.
10. Extreme Programming Methodology
Extreme Programming (XP) is centered around improving software quality and responsiveness to changing customer needs. It emphasizes practices like pair programming, test-driven development, and continuous integration.

Advantages
High-Quality Products
Significant customer involvement and continuous testing ensure high-quality, stable products.
Error Reduction
Pair programming helps cut errors during the development process.
Flexibility
A high level of flexibility allows for immediate implementation of changes.
Clear Code
The code remains clear and comprehensive, improving maintainability.
Timely Delivery
Focus on timely delivery of final products saves costs and time.
Cost Efficiency
Reduces the need for extensive documentation, saving money.
Rational Planning
Helps establish rational plans and schedules, fostering developer commitment.
Customer Involvement
Emphasizes customer involvement, ensuring the product meets user needs.
Disadvantages
Dependence on Team Efficiency
Success relies on the skills and efficiency of the team members.
High Client Engagement
Requires constant client engagement throughout the development process.
High Costs and Time Investment
Involves considerable time and cost investments.
Challenges for Small Teams
It is difficult for small teams to implement due to the need for diverse skills and knowledge.
Focus on Code Over Design
May focus on coding over design, impacting the marketability of the software.
Difficulty in Estimations
It is hard to provide accurate work effort estimates early in the project due to evolving scope and requirements.
Use case
Tech companies, particularly startups and those in the fast-paced internet sector, often employ XP to maintain high quality while adapting quickly to market changes.
11. Joint Application Development Methodology
Joint Application Development (JAD) involves the client or end user in the development process through a series of collaborative workshops, ensuring the final product closely aligns with their expectations.
Advantages
Efficient Information Gathering
JAD allows for the simultaneous collection and consolidation of large amounts of information, which enhances efficiency and accuracy.
Risk Reduction
Collaboration between the company and clients lowers risks, ensuring better alignment and understanding.
High-Quality Output
This method produces large amounts of high-quality information, reducing the costs and time needed for project development.
Conflict Resolution
Proper facilitation resolves differences immediately, improving project cohesion and decision-making.
Multiple Perspectives
Provides a platform to explore various viewpoints, enhancing the quality of the project requirements.
Well-Defined Requirements
Leads to improved system quality through clear and precise requirements, ensuring the end product meets user needs.
Close Communication
Facilitates close communication between team members and clients. Speeds up the development process and ensures alignment.
Enhanced Productivity
Encourages team members to push each other for faster, high-quality deliverables.
Disadvantages
Time-Consuming Planning
Requires significant planning and scheduling, which can be time-consuming for the development team.
High Commitment from Investors
It demands a lot of time and effort from investors, which can be challenging to sustain.
Need for Experienced Personnel
Effective implementation requires trained and experienced professionals, which may not always be available.
Budget Requirements
It can be costly due to the need for extensive planning, facilitation, and experienced personnel.
Use Case
Many e-commerce platforms use Joint Application Methodology (JAD). This method ensures business systems meet the specific needs of customers and stakeholders. Thus, leading to enhanced user experiences and satisfaction. JAD improves requirement-gathering accuracy and user satisfaction by involving users early and often.
12. Lean Development Methodology
Lean Development focuses on maximizing value and minimizing waste throughout the software development process. It applies principles from lean manufacturing to software development, emphasizing efficiency and the elimination of non-value-adding activities.
Advantages
Cost-Effective for Tight Budgets
Lean development is perfect for projects with limited budgets and strict timelines. It focuses on essential tasks, ensuring resources are used efficiently.
Streamlined Processes
Lean development speeds up the process by eliminating waste, such as redundant code, unnecessary documentation, and repetitive tasks.
Rapid Delivery
Lean principles facilitate faster product delivery, enabling teams to bring more functionality to the market in a shorter time.
Scalable for Large Projects
Unlike many other methodologies, Lean development scales to accommodate large projects.
Focus on Core Features
Prioritizing high-value features and core processes ensures the final product meets user needs.
Enhanced Team Motivation
Empowering team members with decision-making authority boosts their motivation and purpose.
Continuous Improvement
Lean development's iterative nature allows for constant refinement and enhancement of the product based on user feedback and testing.
Disadvantages
Dependence on Team Expertise
The success of lean development relies on the discipline and technical skills of the team members. Less experienced teams may struggle to meet the methodology's demands.
Risk of Over-Cutting
Excessive task elimination can lead to a loss of focus on the project’s original objectives, harming the development process.
Potential for Delays
Bottlenecks and low resource levels can cause delays, affecting the project timeline.
Documentation Challenges
Lean development reduces unnecessary documentation. Yet, maintaining detailed records is still essential to cover all project aspects, which places a significant burden on business analysts.
Use case
Tech giants like Toyota have applied lean principles beyond manufacturing, into their IT and software development practices, showcasing significant gains in efficiency and productivity.
How to Select a Software Development Methodology
Selecting the right methodology depends on various factors, including project goals, team structure, and the need for flexibility. It's vital to align the methodology with the project's specific requirements to optimize team performance and product quality.
Impact on Time to Market and Product Quality
The chosen development methodology significantly impacts the time to market and the quality of the software product. A well-aligned methodology can enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and ensure the product meets user needs.
Future Trends in Software Development
Let's talk about where software development trends are heading and it's exciting! The integration of AI and machine learning is starting to shake things up in a big way. We're looking at a future where these technologies could take over a lot of the complex, time-consuming tasks that developers currently handle. They might even help make better decisions and create software that feels more personalized for each user. It's going to be interesting to see how this changes the way we approach software development.
Conclusion
By understanding in detail about software development methodologies, we've uncovered that each methodology brings its own set of rules and benefits to the table. The big takeaway is that there's no one-size-fits-all approach. Each method, whether it's Agile, Waterfall, or something else, has its own playbook and perks. Agile is great when you need to roll with the punches, Waterfall gives you a clear roadmap from start to finish, and Rapid Application Development is all about speed.
Choosing the right method isn't just a technical decision - it can make or break your project. These approaches are like different routes to the same destination. They all aim to turn ideas into real, working software that makes an impact. The trick is picking the path that works best for your team and your project.
At Prioxis, we specialize in custom software development services, offering expertise across a broad spectrum of development methodologies. Our team is committed to understanding your unique business needs and selecting the most effective methodology to bring your software vision to life. With our deep understanding of different development approaches and a commitment to quality, innovation, and client satisfaction, Prioxis is your ideal partner in crafting software solutions that drive success and growth.
Get in touch

