RPA Use Cases for Industries
 Admin
Admin
 Aug 28, 2024
Aug 28, 2024

Table of Content
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is revolutionizing industries by delivering efficiencies once thought impossible. As businesses strive for streamlined operations, RPA emerges as a key innovation. This technology holds the potential to transform various sectors, reducing costs and boosting productivity.
In this detailed article, we’ll explore the significant benefits of RPA. We’ll present practical use cases and examples to show its crucial role in today’s industries. Whether you lead a manufacturing firm, a financial institution, a healthcare provider, or a retail business, RPA could be a game-changer for you.
Understanding Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is software that automates manual, repetitive tasks. It mimics human actions to execute processes, cutting the need for human involvement. This automation is ideal for tasks that are repetitive, predictable, and based on clear rules.
The main advantage of RPA is its ability to reduce human errors. It also boosts business efficiency and productivity. A report by Gartner highlights that by the end of 2022, 85% of large corporations had adopted RPA. Another forecast from Forrester predicts that the global RPA market will reach $22 billion by 2025. These figures show how rapidly RPA is being embraced across various industries.
What Makes a Good RPA Use Case?
RPA works best for digital tasks that are high-volume, repetitive, and rule-based. The ideal RPA use case involves tasks with predictable outcomes and processes that follow clear rules. This is particularly true for tasks where human involvement adds little value.
Take invoice processing in manufacturing as an example. This task involves handling large amounts of data. It’s time-consuming and prone to errors if done manually. Automating this process with RPA ensures prompt and right payments. It also frees up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
Comprehensive RPA Use Cases Across Multiple Industries
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a powerful tool that can automate repetitive tasks across various industries, driving efficiency, reducing errors, and enabling employees to focus on more strategic activities. Below are detailed use cases for RPA across different industries:
1. Manufacturing
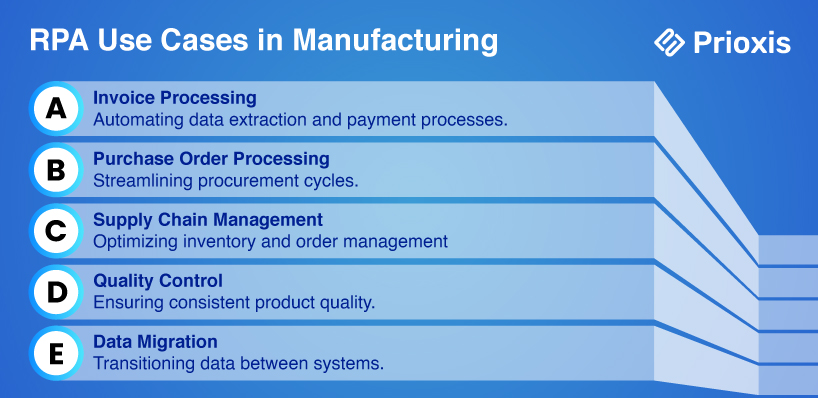
a. Invoice Processing
Manufacturing companies deal with large volumes of invoices from multiple vendors. RPA can automate the entire process—from data extraction using OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to confirming and entering data into financial systems. This reduces manual errors, ensures prompt payments, and enhances vendor relationships.
b. Purchase Order Processing
RPA can automate the creation and management of purchase orders by extracting data from emails or PDFs, confirming it, and entering it into ERP systems. This automation reduces manual entry errors and accelerates procurement cycles.
c. Supply Chain Management
RPA can automate supply chain tasks like inventory tracking, order processing, and supplier communications. It ensures best inventory levels, reduces stockouts, and minimizes delays in the supply chain.
d. Quality Control
In manufacturing, keeping consistent product quality is crucial. RPA bots can automate data collection during production and perform real-time analysis to ensure products meet quality standards, reducing the likelihood of defects.
e. Data Migration
When transitioning to new systems, RPA can automate the migration of data from legacy systems to modern platforms, ensuring accuracy and reducing the risk of data loss.
2. Financial Services
a. Customer Onboarding
RPA can streamline the customer onboarding process by automating data entry, document verification, and account setup. This reduces the onboarding time, improves accuracy, and enhances customer satisfaction.
b. Fraud Detection
RPA can check transactions in real-time, find suspicious activities, and flag them for further investigation. This automation enhances security and helps financial institutions follow regulatory requirements.
c. Loan Processing
RPA can automate the loan processing workflow, from application submission to approval. This reduces manual intervention, accelerates loan approvals, and improves the overall customer experience.
d. Accounts Payable and Receivable
RPA can automate the accounts payable and receivable processes, including invoice processing, payment reconciliation, and data entry. This ensures prompt payments and improves cash flow management.
e. Compliance Reporting
RPA can generate and give compliance reports automatically, ensuring accuracy and prompt adherence to regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of penalties.
Learn Further: RPA in Finance
3. Healthcare
a. Patient Data Management
RPA can automate the entry, updating, and retrieval of patient records, ensuring that healthcare providers have accurate and up-to-date information. This improves patient care and reduces administrative burdens.
b. Appointment Scheduling
RPA can improve appointment scheduling by matching physician availability with patient preferences, reducing no-shows and improving operational efficiency.
c. Claims Processing
RPA can speed up insurance claims processing by automatically extracting and verifying data, leading to faster reimbursements and fewer errors in the healthcare revenue cycle.
d. Inventory Management
RPA can automate the tracking of medical supplies, ensuring that healthcare facilities keep optimal inventory levels and avoid shortages or overstock situations.
e. Compliance Reporting
Healthcare providers must adhere to strict regulatory requirements. RPA can automate the generation and submission of compliance reports, ensuring accuracy and reducing the administrative burden on staff.
4. Retail
a. Inventory Management
RPA can check stock levels in real-time and automatically place orders when inventory runs low. This ensures that products are always available for customers, reducing the risk of stockouts.
b. Price Comparison
Retailers often need to compare prices across vendors to ensure competitive pricing. RPA can automate this process, allowing businesses to quickly compare prices and make informed purchasing decisions.
c. Customer Support
RPA can automate responses to common customer queries, categorize support tickets, and route them to the right departments. This improves response times and customer satisfaction.
d. Order Processing
RPA can automate the entire order processing workflow, from receiving orders to updating inventory and generating shipping labels. This reduces manual effort and ensures quick and right order fulfillment.
e. Marketing Automation
RPA can help retailers personalize their marketing efforts by automating tasks such as customer segmentation, email campaign management, and loyalty program administration.
5. Human Resources
a. Payroll Processing
RPA can automate the payroll process by collecting data from various systems, confirming timesheets, calculating earnings and deductions, and generating paychecks. This reduces errors and ensures employees are paid on time.
b. Recruitment
RPA can streamline recruitment by automating resume screening, interview scheduling, and candidate communication. This allows HR professionals to focus on talent acquisition and strategy.
c. Employee Onboarding
RPA can automate the onboarding process, ensuring that all necessary paperwork is completed, and new hires are set up in the system quickly and efficiently.
d. Compliance Reporting
HR departments must adhere to various regulatory requirements. RPA can automate the generation of compliance reports, ensuring accuracy and timeliness.
e. Employee Data Management
RPA can automate the management of employee records, including updating personal information, tracking performance metrics, and managing benefits administration.
6. Telecommunications
a. User Account Verification
Telecom companies handle large volumes of new account registrations daily. RPA can automate the verification process, ensuring accuracy and reducing the time required to activate new accounts.
b. Network Monitoring
RPA can automate the monitoring of network performance, detecting and reporting issues in real-time. This helps telecom companies support high service quality and minimize downtime.
c. Number Porting
RPA can streamline the process of number porting, which involves transferring a phone number from one provider to another. Automating this process reduces errors and accelerates the transfer.
d. Billing and Payments
RPA can automate billing and payment processes, including generating invoices, processing payments, and updating customer accounts. This improves efficiency and reduces the risk of errors.
e. Customer Support
RPA can help in customer support by automating responses to common inquiries, routing requests to the right departments, and updating customer records.
7. Insurance
a. Claims Processing
RPA can automate the claims processing workflow, from first submission to final approval. This reduces the time needed to process claims, improves accuracy, and enhances customer satisfaction.
b. Policy Management
RPA can automate the management of insurance policies, including renewals, cancellations, and updates. This ensures right and up-to-date policy information.
c. Underwriting
RPA can streamline the underwriting process by automating data collection, risk assessment, and decision-making. This reduces the time needed to underwrite policies and improves consistency.
d. Fraud Detection
RPA can analyze claims data to detect patterns indicative of fraud. By flagging suspicious claims, RPA helps insurance companies reduce fraud and associated costs.
e. Regulatory Compliance
RPA can automate the generation and submission of regulatory reports, ensuring compliance with industry standards and reducing the risk of penalties.
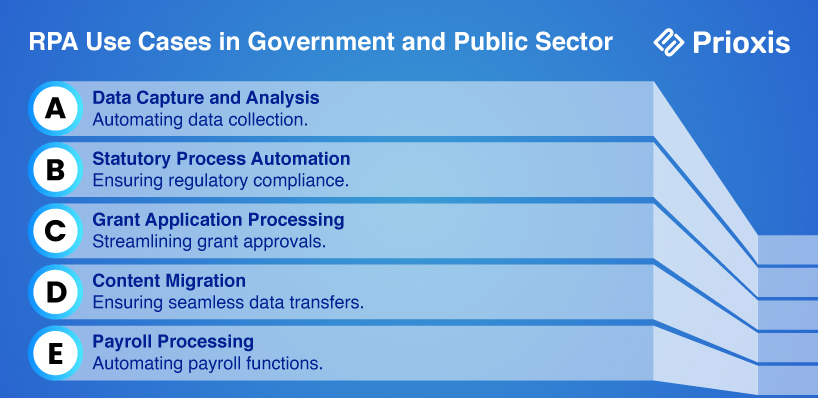
8. Government and Public Sector
a. Data Capture and Analysis
RPA can automate the collection and analysis of data from surveys, censuses, and other sources. This helps government agencies make informed decisions based on right and up-to-date information.
b. Statutory Process Automation
Government agencies often deal with complex statutory processes that require precision and consistency. RPA can automate these processes, ensuring compliance and reducing manual errors.
c. Grant Application Processing
RPA can streamline the processing of grant applications by automating data extraction, validation, and decision-making. This reduces the time needed to process applications and improves accuracy.
d. Content Migration
When updating systems or websites, RPA can automate the migration of content from old platforms to new ones, ensuring data integrity and reducing the risk of errors.
e. Payroll Processing
RPA can automate payroll processing for government employees, ensuring exact and prompt payments while reducing the administrative burden on payroll staff.
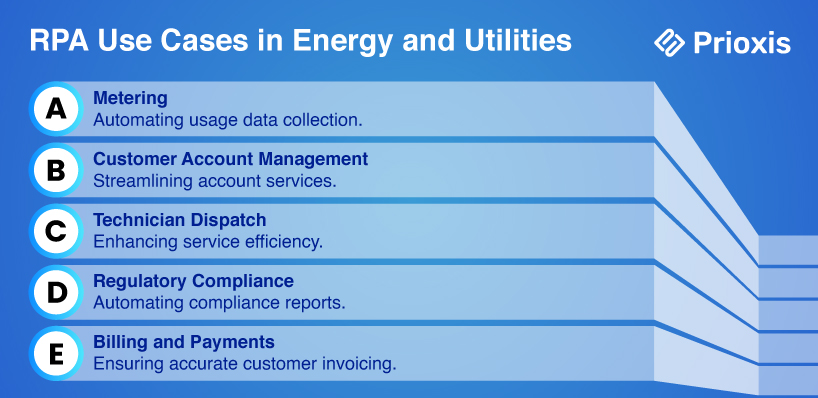
9. Energy and Utilities
a. Metering
RPA can automate the reading of meters and the recording of usage data, ensuring correct billing and reducing the need for manual meter readings.
b. Customer Account Management
RPA can automate the management of customer accounts, including updates, billing, and payments. This improves customer service and reduces errors.
c. Technician Dispatch
RPA can improve the dispatch of technicians by automating scheduling based on availability, location, and urgency. This ensures prompt service and reduces downtime.
d. Regulatory Compliance
Energy and utility companies must follow strict regulatory requirements. RPA can automate the generation and submission of compliance reports, reducing the risk of penalties.
e. Billing and Payments
RPA can automate the billing and payment processes, including generating invoices, processing payments, and updating customer accounts. This improves efficiency and reduces errors.
10. Logistics and Supply Chain
a. Shipment Scheduling
RPA can automate the scheduling of shipments by extracting data from various sources and coordinating logistics. This reduces manual errors and ensures prompt deliveries.
b. Delivery Tracking
RPA can check shipment statuses in real-time and send alerts to stakeholders when deliveries reach specific checkpoints or encounter delays.
c. Order Management
RPA can automate the management of orders, including processing, tracking, and fulfillment. This ensures accuracy and speeds up the delivery process.
d. Inventory Tracking
RPA can check inventory levels across multiple locations, triggering reorders when stock runs low. This helps support best inventory levels and reduces the risk of stockouts.
e. Freight Management
RPA can automate the management of freight, including load matching, route optimization, and documentation. This reduces manual effort and improves the efficiency of freight operations.
Final Thoughts
RPA's versatility allows it to be applied across various industries, automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and freeing up employees for more strategic work.
Whether you're in manufacturing, financial services, healthcare, retail, or any other industry, there are RPA solutions that can help streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
At Prioxis, we specialize in helping businesses harness the power of RPA to drive efficiency and innovation. Our team of experts will work closely with you to find the best automation opportunities, design customized RPA solutions, and ensure seamless integration into your existing processes.
Get in touch