Expertise
Banking took seven decades to fully digitize, with incremental innovations from ATMs, magnetic chips to mobile apps, digital banking, UPI, QR codes and many more. In contrast, the insurance industry, which is long associated with manual, paperwork-heavy processes are now on the brink of a significant technological transformation, thanks to Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Imagine hiring insurance advisors, account managers, or employees who:
- Work 24/7 without breaks
- Never make data entry mistakes
- Process claims in minutes, not hours
- Don’t get tired or need a vacation
- Cost a fraction of a regular employee
RPA is making these possible, empowering insurers to deliver faster, more reliable customer service at a reduced cost.
What is RPA in Insurance?
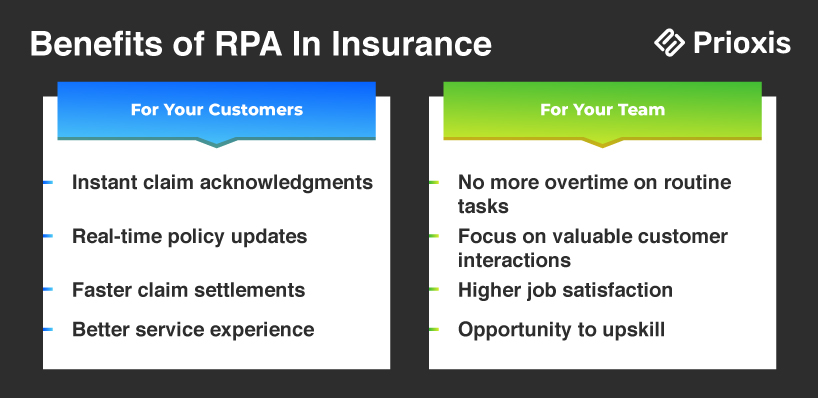
RPA in Insurance is changing how insurance companies work. It helps with tasks like reviewing new policies, signing up customers, handling customer service, and processing claims. By letting bots do these time-consuming jobs, insurance companies can work faster, be more efficient, and give customers a better experience.
Insurance automation also handles tasks like validation, data processing, and routine management. According to research, around 25% of insurance tasks could be fully automated by 2025.
If you’re considering RPA for your insurance business, this guide will cover everything you need to know. From its primary use cases to the benefits of automation, this blog dives into how RPA can help insurers tackle critical tasks like claims processing, policy administration, underwriting, fraud detection, compliance, policy cancellation, and query resolution.
Opportunity Cost of Not Implementing RPA in Insurance
The insurance industry relies heavily on data-intensive processes. Tasks such as claims processing, policy management, customer onboarding, and regulatory compliance are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to error when handled manually. For example, insurers frequently face:
- Lengthy Claims Processing Manual data entry and cross-verification slow down claims approval, frustrating policyholders.
- High Operational Costs Staff time spent on repetitive tasks can divert resources from customer-centric activities.
- Data Accuracy and Compliance Risks Handling vast amounts of personal and financial data comes with a high risk of error and regulatory consequences.
The Hard Truth About Traditional Insurance Operations:
- 60% of your staff's time is spent on repetitive tasks
- Each manual claim process costs you $15-25 in pure processing time
- Human errors in policy administration cost the industry $3.4 billion annually
- 67% of customers switch insurers due to poor service experience
Read Further: RPA In Finance
Use Cases of RPA in Insurance
1. Automate Claim Processing
The claims' processing lifecycle is one of the most resource-intensive areas in insurance, involving tasks like data verification, policy validation, and payout calculations. Traditionally, these steps are handled manually like data gathering, validation, policy checks, and payment calculations, which increases the risk of errors, inefficiencies, and customer dissatisfaction.
- Data Collection and Verification RPA bots can extract data from documents using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to read claims forms, scan them for required information, and validate details against policy terms. This automation cuts down the time spent manually handling claims.
- Automated Decision-Making Bots use pre-set rules to approve or deny claims based on factors such as policy details, coverage limits, and claim history.
- Customer Communication RPA can send instant updates to customers, informing them about their claim status, expected timelines, and any required follow-ups.
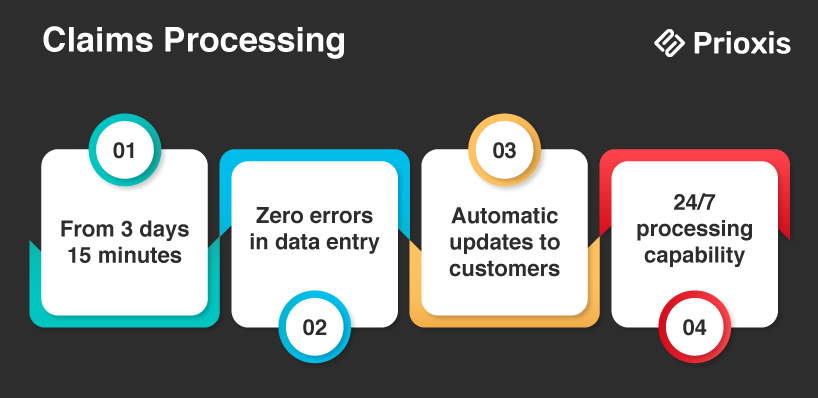
Without RPA
- Your staff manually enters data from multiple documents
- Claims pile up during busy periods
- Customers call constantly for status updates
- Processing takes 2-3 weeks on average
With RPA
- Documents are automatically scanned and processed
- Data enters your system instantly
- Customers receive automatic updates
- Claims are processed in hours, not weeks
- Your staff only handles complex cases needing human judgment
Example: A bot can scan and validate documents (like medical records or accident reports), cross-check with policy terms, and approve or reject claims based on pre-established guidelines, all within minutes. Using RPA, you can also reduce claim settlement time by up to 60%, by accelerating faster payouts and enhancing customer satisfaction. This efficiency also allows insurance firms to handle larger claim volumes with the same resources.
2. Policy Administration
Policy administration includes end-to-end management of insurance tasks like issuing new policies, updating customer data, and managing renewals. Given the volume of policies managed daily, errors or delays in policy administration can lead to customer frustration and potential regulatory issues.
- Streamlining Policy Issuance and Renewals Bots use RPA and machine learning (ML) to update policy information, handle renewals, and verify customer data. For instance, when a customer requests a policy change, bots can pull relevant data, make updates across systems, and notify the customer.
- Data Consistency and Updates RPA ensures consistent updates across systems by synchronizing policy details and customer data in real-time.
- Regulatory Compliance RPA bots validate policy details against regulatory standards, ensuring that policies meet compliance requirements.
Without RPA
- Staff spends hours copying data between systems
- Policy updates take days to process
- Renewal notices often go out late
- Human errors cause customer complaints
With RPA
- Data automatically syncs across all systems
- Policy updates happen in real-time
- Renewal notices go out on schedule
- Accuracy rate jumps to 99.9%
Example: For policy renewals, bots can gather necessary information, process renewals, and update policy status without any manual input, reducing errors and send reminders to policyholders for efficient and error-free management.
3. Underwriting:
Underwriting is one of the most data-driven areas in insurance, requiring underwriters to evaluate risk by analyzing large data sets from multiple sources. The process traditionally involves extensive data gathering and analysis, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
How RPA Helps
- Automated Data Collection RPA bots can gather data from financial reports, health records, and credit scores using OCR, then organize it for underwriters to review. Bots also perform initial risk assessments based on specific criteria, leaving only complex cases for human underwriters.
- Preliminary Risk Assessment RPA can perform initial risk evaluations based on set criteria, helping underwriters focus on more complex cases.
- Data Accuracy and Consistency By reducing manual data handling, bots ensure that underwriters work with accurate, up-to-date information.
Without RPA
- Underwriters waste time gathering basic information
- Risk assessments take days
- Inconsistent decision-making
- Valuable underwriters stuck doing basic tasks
With RPA
- All relevant data automatically gathered and organized
- Initial risk assessment completed in minutes
- Consistent application of underwriting rules
- Underwriters focus on complex cases and relationship building
Example: For high-risk policy applications, bots can pull relevant data, perform a preliminary assessment, and flag cases that need deeper review, reducing underwriting turnaround times by as much as 70%.
4. Fraud Detection
Insurance fraud is a significant issue that costs insurers billions of dollars annually. Identifying fraudulent claims requires sifting through vast amounts of data, identifying anomalies, and flagging suspicious cases for further investigation.
How RPA Helps
- Pattern Recognition RPA bots scan claims data for patterns that match known fraud indicators. ML models help by continuously improving the accuracy of fraud detection, making it easier to catch fraudulent claims early.
- Cross-Verification RPA bots verify claim details by cross-referencing with external sources, such as public records and social media profiles, enhancing the accuracy of fraud detection.
- Automated Alerts Whenever a claim is flagged as potentially fraudulent, RPA sends alerts to the fraud management team for immediate review.
Without RPA
- Limited fraud checking due to time constraints
- Fraud often discovered after payment
- Random sampling misses many cases
- High losses from undetected fraud
With RPA
- Every claim automatically screened for fraud indicators
- Suspicious patterns flagged instantly
- 100% of claims checked
- Significant reduction in fraud losses
Example: A bot could compare claims against historical data, detect unusual patterns like frequent claims from a single policyholder, and flag these cases for manual review. These bots reduce fraud cases by up to 40% and ensure a fair claims process for genuine customers.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Insurers face strict regulatory requirements, which often demand regular reporting and accurate record-keeping. Manual compliance management is not only time-consuming but also increases the risk of costly errors and fines.
- Automated Report Generation RPA bots pull data from different systems, validate it, and compile it into regulatory reports. NLP (Natural Language Processing) helps extract data from unstructured documents, ensuring all relevant information is captured.
- Audit Trail Creation RPA creates detailed audit trails for all automated processes, simplifying regulatory audits and ensuring transparent record-keeping.
- Data Consistency RPA verifies data accuracy across systems, reducing the risk of errors in compliance reporting.
Without RPA
- Time-intensive manual reporting with a high chance of errors
- Compliance audits delayed due to slow data gathering
- Higher risk of non-compliance penalties due to incomplete records
- Resources tied up in routine compliance tasks, slowing other operations
With RPA
- Reports automatically generated with real-time data
- Data validated for accuracy and regulatory standards compliance
- 100% of required documents readily available for audits
- Significant reduction in compliance risks and penalties
Example: For a quarterly regulatory report, RPA bots can collect data from various departments, validate its accuracy, and compile it into a standardized report format for submission, all within compliance guidelines.
6. Policy Cancellation
Policy cancellation involves verifying eligibility, processing refunds, and ensuring that records are updated consistently. RPA bots can check eligibility rules, calculate pro-rated refunds, and notify customers automatically. OCR can assist by digitizing any required documents for processing. Manual handling of these steps can introduce delays and errors, impacting customer satisfaction.
How RPA Helps
- Eligibility Verification RPA bots validate cancellation requests against policy terms, ensuring that each cancellation request meets eligibility criteria.
- Refund Processing Bots calculate pro-rated refunds automatically, reducing the chance of calculation errors and speeding up the refund process.
- Automated Customer Notifications Once a policy is canceled, bots send automated notifications to customers, providing them with status updates and any follow-up actions needed.
Without RPA
- Delayed processing due to manual eligibility checks
- Errors in pro-rated refund calculations, leading to customer dissatisfaction
- Customer notifications are often missed or delayed
- Higher operational costs due to repetitive manual steps
With RPA
- Instant eligibility verification and automated pro-rated refunds
- Accurate updates to policy status and quick processing
- Customers automatically notified at each cancellation stage
- Reduced time and costs with a fully automated cancellation process
Example: A bot could automatically verify a cancellation request, process refunds, update policy status, and inform the customer, completing the entire process within minutes in a single workflow, reducing processing times by up to 50%.
7. Query Resolution
Customer queries range from policy details to claim status updates and often require quick response times. Traditional call centers and support teams are overwhelmed by routine inquiries that detract from handling more complex customer needs.
How RPA Helps
- Automated Responses to Routine Queries NLP allows bots to understand and respond to customer questions. RPA bots can retrieve answers from internal databases and deliver them to customers in real time, escalating complex queries to agents if needed.
- Real-Time Status Updates RPA keeps customers updated in real-time by providing status updates for claims or policy applications, enhancing transparency.
- Escalation of Complex Issues For more complex inquiries, RPA escalates the issue to a human agent, ensuring that each customer receives the appropriate level of assistance.
Without RPA
- Long wait times for customers due to high volume of routine queries
- Support teams bogged down with repetitive questions
- Limited resources available for complex inquiries requiring human attention
- Higher risk of inconsistent responses and customer dissatisfaction
With RPA
- Routine queries (e.g., claim status, policy details) answered instantly
- Automated escalation of complex issues to human agents
- 24/7 availability, reducing customer wait times significantly
- Consistent, accurate responses, leading to improved customer satisfaction
Example: By automating routine customer interactions, RPA can reduce query response times by up to 80%, allowing customer service agents to focus on more complex customer needs. A bot could handle routine inquiries such as “What is the status of my claim?” by accessing the relevant database and providing real-time responses to customers.
Advanced Technologies Enhancing RPA in Insurance
1. Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
OCR technology allows RPA to read and process text from scanned documents, PDFs, and images. This is particularly useful in insurance, where a lot of information still exists in physical forms, like handwritten claims forms, medical records, or policy documents. OCR transforms these paper documents into digital data, which RPA can then work with seamlessly.
- Reduces manual data entry
- speeds up claims and policy updates.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP allows RPA to understand and respond to human language, ideal for automating customer queries or analyzing text-heavy documents.
- Enables bots to handle customer questions
- extract details from text
- improve fraud detection.
3. Machine Learning (ML)
ML helps RPA learn from past data, allowing it to identify patterns and make decisions which is useful for fraud detection and risk assessment.
- Makes bots smarter over time
- Enhancing fraud prevention and compliance.
4. AI-Driven Analytics
AI-driven analytics allows RPA to not just process data, but also analyze it and generate insights that can drive business decisions. In the insurance industry, this can include understanding claim trends, predicting customer needs, and assessing operational performance.
- Helps Insurers Make Data-driven Decisions
- Improves Operational Efficiency
5. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) goes beyond OCR by adding AI to understand the context of a document. IDP can handle documents that are complex or have a lot of unstructured data, like multi-page health records or itemized bills, which are common in insurance.
- Allows Bots to Process Complex Data Accurately
- Essential For Underwriting and Claims
6. Computer Vision
Computer Vision is the AI technology that allows RPA to "see" and interpret visual data, like images and videos. In insurance, computer vision can be used in claim assessments or property inspections, leading RPA to analyze photos and detect details about damage or assets.
- Automates Visual Tasks
- Reducing The Need for Physical Inspections
- Speeding Up Claims
The Cost of RPA in Insurance: Beyond Licensing
The cost of implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in insurance depends largely on the number of bots used and the software required. Implementing RPA in insurance involves more than just licensing, which accounts for 25-30% of the total cost. While each bot costs between $5,000 and $15,000, insurers should also budget for:
- Annual Renewal Fees Keeps bots updated.
- Expert Training or Hiring Needed for effective operation.
- Consulting and Setup Fees Facilitates smoother implementation.
- Infrastructure and Integration Costs Supports reliable bot function.
- Maintenance Keeps bots operating efficiently.
Learn more about The Cost of Automation (RPA) here: RPA Implementation Cost
Wrapping Up
In an industry built on trust, efficiency, and customer satisfaction, the advantages of RPA in insurance are undeniable. Manual processes in claims, policy administration, underwriting, and compliance slow down operations and lead to costly errors. It is an automation solution that minimizes these problems and offers exactly that, by automating repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and accelerating key processes.
Without RPA, insurers risk high operational costs, lengthy claims processing, and data accuracy issues, which can push customers to competitors. However, by implementing RPA, insurers can deliver fast, error-free service, retain high-value customers, reduce insurance and claims related frauds, and stay compliant without the constant burden on staff.
As we’ve explored in this guide, the benefits of RPA are measurable and impactful. If you’re ready to drive your insurance operations forward, our team can help make automation a seamless addition to your strategy. Reach out to us today to discover how RPA can enhance your business, improve customer satisfaction, and set you apart in the insurance market.