Patient Portal Development for Healthcare Providers: A Guide
 Admin
Admin Software Development
Software Development Jan 17, 2025
Jan 17, 2025

Table of Content
Patient portals have become vital tools in changing the healthcare landscape, as they enhance patient engagement and streamline the administrative workflow of healthcare providers. Since their establishment in the late 90s, these healthcare platforms have become essential for both small clinics and large health systems to enable them to deliver advanced treatments and effectively place patients at the forefront.
Nevertheless, many of the current patient portals in healthcare have not met the needs of current users. For older adults, those less comfortable with technology, and perhaps others, this results in an inability to access crucial healthcare data.
In this guide, we will explore the essential elements of effective patient portal development. We will discuss the importance of creating a user-friendly experience, the technology stack needed for implementation, and the key features that make a patient portal truly stand out.
What is a Patient Portal?
A patient portal is an interface accessible through mobile or online, where patients can view their personal health information and medical services 24/7 from any web-enabled device. It links people and healthcare providers by allowing users to view their medical data, appointments, medications, and other medical bills.
For instance, a patient can get test results of a recent visit through a patient portal without visiting the healthcare institution for a follow-up consultation. Another patient might want a virtual consultation with a clinician since they are unwell and would not want to come in for an appointment at the healthcare facility.
What is a patient portal in health care convenient for patients and providers alike-it saves their precious time and streamlines communication for both.
Types of Patient Portals
There are two major types of patient engagement portals available in the market:
1. Standalone Patient Portal
Standalone patient portals are software solutions that are focused on a limited number of functionalities but are widely used by healthcare institutions. Typically, these portals provide one key function, such as viewing lab test results or scheduling an appointment.
Such importers are not included with larger data exchanges, like Electronic Health Records EHR or even Hospital Management System HMS. Stand-alone online patient portals of such independent practice providers often only include smaller operators, including freestanding and independent pharmacies, private laboratories, boutique clinics, and most local medical office settings.
The architecture of standalone patient portals is relatively simple, which means lower development effort and investment. This simplicity allows even less-experienced programming teams to develop standalone healthcare software quickly. Therefore, these portals are generally more affordable for smaller businesses.
2. Integrated Patient Portal
Integrated patient portals, also known as connected or tethered portals, act as an interface for a bigger medical system such as EHRs or HMSs. Such portals are made for more complex systems of healthcare institutions.
For bigger facilities, integrated patient portals allow direct access to the patient database managed by the organization or medical facility. This connection allows the software to provide a broad range of services and functions to healthcare providers.
Integrated patient portals would take more time and effort in terms of various features and integrating with existing bigger systems. Development costs for the integrated patient portal are higher as compared to stand-alone portals. Integrated patient portals can also significantly contribute to bigger digital transformation programs by including the approaches of development of hospital management software.
Benefits of Patient Portal for Health Providers & Patients
Patient portals are some of the most important healthcare IT solutions that make it easier to access medical records and enhance communication between patients and healthcare providers. Here are the key patient portal benefits:
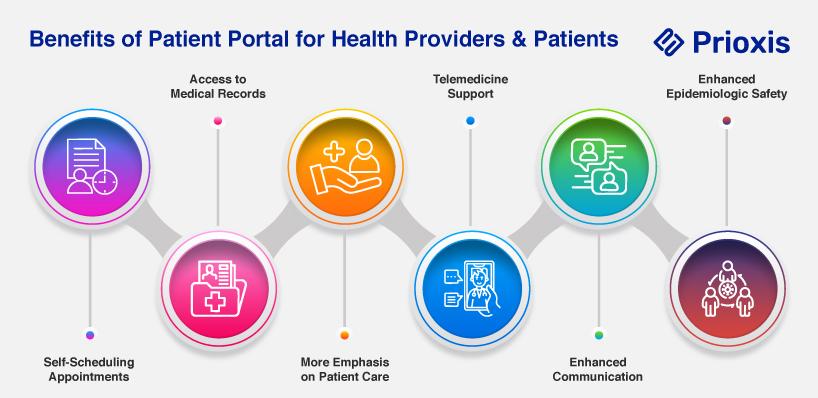
1. Self-Scheduling Appointments
Patient
The patient can schedule appointments online, which is convenient and increases satisfaction and loyalty by reducing wait times and making same-day or next-day appointments possible.
Healthcare Provider
Providers can set up time slots for self-scheduling appointments, and staff can then manage their work more effectively without scheduling conflicts.
2. Access to Medical Records
Patient
Patients can access their medical records online, and this will help them adhere to medication and reduce emergency room visits due to errors in their records.
Healthcare Provider
Providers get quick access to patient records, and this improves care for chronic patients and streamlines payment processing, lab results, and prescription requests.
3. More Emphasis on Patient Care
Patient
Portals decrease the number of in-person visits and provide extensive resources for managing health, so patients are more satisfied with their treatment.
Healthcare Provider
Patient portals promote patient-centered care, enabling patients to be in control of their health, enhancing retention, and making billing easy.
4. Telemedicine Support
Patient
Patients can schedule online appointments for medication changes, saving time and ensuring timely care.
Healthcare Provider
Portals minimize unnecessary visits to the clinic by providing a secure messaging service for minor complaints, thus allowing the providers to attend to serious cases.
5. Enhanced Communication
Patient
Portals facilitate communication, thus patients can communicate with doctors at any time using secure messaging or video calls for easy access to information.
Healthcare Provider
They make the administrative processes smooth, enhance patient engagement, and give doctors key insights into patient health for timely interventions.
6. Enhanced Epidemiologic Safety
Patient
Patients can track health metrics, which allows them to continuously monitor their vital signs from home, especially supporting vulnerable patients.
Healthcare Providers
Managing foot traffic helps minimize the risk of infectious infections since patient portals provide a safer healthcare setting.
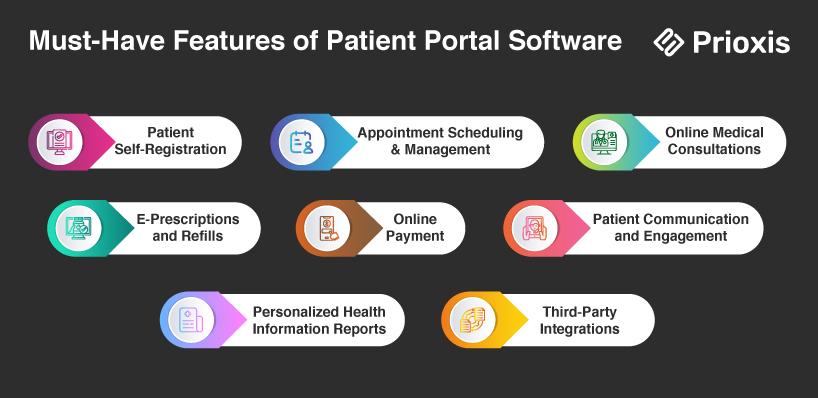
Must-Have Features of Patient Portal Software
During the development of a patient portal, must-haves are those features that help improve usability and enhance the overall patient experience. Here are the must-haves:
1. Patient Self-Registration
This feature enables the patient to create his or her account easily and securely, thereby allowing easy access to health information.
2. Appointment Scheduling and Management
The feature helps manage appointments schedule, rescheduling, or even cancellations through online channels. This feature is convenient and reduces administrative burdens.
3. Online Medical Consultations
Allows the patient to visit the healthcare provider virtually hence not physically going to the clinic for health care.
4. E-Prescriptions and Refills
This allows a health provider to communicate prescriptions to the patient, thus making it easy for the patient to get a prescription filled or get a refill.
5. Online Payment Feature
This allows the patient to make payments directly for services received. This improves convenience and eases the billing process.
6. Patient Communication and Engagement
Provides safe messaging capabilities for patients to interact with their healthcare providers, which encourages engagement and prompt responses to questions.
7. Personalized Health Information Reports
Provides personalized health reports based on the patient's medical history, thus enabling patients to better understand their health status and treatment plans.
8. Third-Party Integrations
Guarantees interoperability with other healthcare systems and applications, allowing for the easy sharing of data and better functionality across platforms.
Patient Portal Development Challenges
The development of a patient portal encompasses a few key challenges that require careful planning:
1. Understanding User Needs
Tailoring the user experience to meet the diverse needs of patients is crucial. Conditions like eating disorders or mental health issues require different approaches. User research, such as surveys and interviews, can be conducted to ensure the portal meets varied needs effectively.
2. Ensuring Inclusivity
It should create an inclusive environment. For instance, pre-sets of avatars in a group chat help to reduce the anxiety of sharing personal images of those who may not want to. Accessibility by people with disabilities, such as voice-activated control for the blind, should be incorporated to improve usability.
3. Compliance and Technical Issues
Navigating HIPAA compliance is very complex as the regulations set very strict parameters for handling sensitive information. Thus, engaging the services of legal and compliance experts right from the start of development would help handle the requirements effectively. Moreover, legacy systems, like Electronic Medical Records (EMR), also present challenges since their technology is somewhat archaic.
4. Technology Selection
Therefore, choosing the proper technology for sustainable telemedicine, especially video consulting features, plays a significant role. The most effective analysis by discovery phase helps to ensure technology stacks are less expensive and can scale over the long term.
How to Design a Patient Portal: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Specify the Needs and Features of Your Patient Portal
Identify the specific needs and features for your patient portal, including appointment scheduling, access to medical records, e-prescriptions, and secure communication. Engage with healthcare providers and patients to gather input.
2. Choose a Healthcare Software Development Company
Select a trustworthy healthcare software development company that has experience in the development of patient portals. Engage closely with their team so that they fully understand your vision and requirements.
3. Design UX/UI Plan
Develop an intuitive user experience and user interface design. The emphasis should be on accessibility and usability, making sure that the portal is easy to navigate for every user, even those with disabilities. Include input from potential users during the design process.
4. Development and Integration
Start the development phase where the technical team develops the portal based on the requirements and design set. The integration with the existing systems like EHR and billing software must be smooth to ensure a coherent user experience.
5. Testing of the Patient Portal Apps
Perform rigorous testing of the portal to find any errors or problems and resolve them. Various methods of testing can be performed to test it completely, including UAT. Thus, all requirements can be ensured with proper portal functioning without creating difficulties for users.
6. App Delivery & Maintenance
After completing the testing, and based on the changes made in the application, deploy the patient portal to its users. Formulate a maintenance plan for updates, security-related issues, and user complaints, which can make the portal user-friendly over time.
Cost of Patient Portal Software Development
Setting up a patient portal involves a lot of investment, and the cost will vary widely depending on several factors. It's not easy to come up with an exact figure for patient portal development; however, based on market trends and project complexity, we can give an approximate overview.
Approximate Cost Breakdown
- Large, Complex Patient Portal ~$200,000 - $300,000
This type usually comes with advanced functionalities for doctors, patients, and administrative staff.
- Native App for one platform (iOS, for instance) ≈ $120,000 - $150,000
One platform application for a specific operating system.
- Native Apps for both iOS and Android ≈ $160,000 - $220,000
Developing an application for both platforms requires more effort and time.
The cost of developing custom patient portal software is generally between $120,000 to $150,000 for a single native app; for example, iOS. For iOS and Android, the cost goes from $160,000 to $220,000 with a unified backend. The price can even go as high as $200,000 to $300,000 for large-scale portals because of their numerous features.
Final Thoughts
Although patient portals have been around for a long time, the majority of them have failed to satisfy consumers' expectations due to poor user experience and integration complexity. Collaboration with the right software development business, on the other hand, can result in the creation of bespoke patient portal solutions that not only meet but exceed, customer expectations.
In-house development of a unique patient portal can result in a variety of benefits, including improved communication between patients and doctors, quicker access to medical records, and increased patient and provider satisfaction. As the healthcare environment advances, user-friendly and integrated solutions will be the most effective approach to produce positive patient experiences and efficient operational processes.
Get in touch