Table of Content
For businesses to remain scalable, cost-efficient, and competitive, cloud adoption is essential. Amid the myriad of choices, one critical decision stands out: Should your business opt for a multi-tenant or single-tenant SaaS architecture? Understanding the nuances between these two models of SaaS application development is vital. This guide breaks down the differences, benefits, and drawbacks of each SaaS architecture, helping you make an informed choice that aligns with your business needs and security requirements.
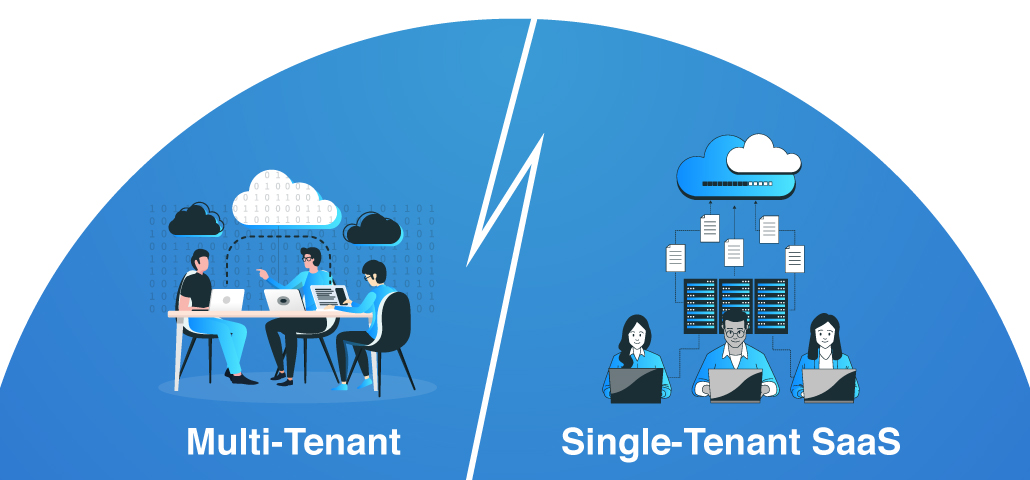
Imagine choosing between renting an apartment in a bustling complex or buying a single-family home. Both options offer shelter, but the experience is vastly different. Similarly, in the SaaS world, multi-tenant and single-tenant architectures provide different ways to deploy and manage software applications in the cloud.
Single-Tenant Architecture means each customer has their own dedicated instance of the software and its supporting infrastructure. Think of it as having your own house—complete control, customization, and isolation from others. Multi-Tenant Architecture, on the other hand, allows multiple customers to share the same software instance and infrastructure, much like sharing an apartment building's amenities.
The architecture you choose impacts everything from cost and scalability to security and compliance. For instance, 82% of cloud breaches are attributed to misconfigurations—a statistic that underscores the importance of understanding how your SaaS model handles security.
Whether you’re running a startup looking to minimize costs or a large enterprise needing stringent security measures, the choice between multi-tenant and single-tenant architectures can significantly influence your operational efficiency and bottom line.
Single-Tenant Architecture offers a unique environment for each customer, providing several compelling benefits:
1. Enhanced Data Security
With a single-tenant model, your data is isolated from other customers. This isolation minimizes the risk of data breaches affecting multiple organizations, making it ideal for industries with stringent compliance requirements like healthcare and finance. For example, hospitals managing patient data under HIPAA regulations often prefer single-tenancy to ensure data privacy and security.
2. Greater Customization
Single-tenancy allows for extensive customization of the software and infrastructure. You can tailor the application to meet specific business needs without worrying about compatibility issues with other tenants. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses that require unique workflows or integrations.
3. Improved Performance and Dependability
Having a dedicated environment ensures that resources are always available when you need them. Unlike multi-tenant setups where resource contention can occur, single-tenancy guarantees consistent performance, which is crucial for mission-critical applications.
4. Portability and Control
Migrating data becomes simpler since each tenant has their own dedicated database and instance. This control over the environment allows for easier data management and portability, ensuring that you’re not tied down by a shared infrastructure.
However, these benefits come with some downsides:
Multi-Tenant Architecture is designed to serve multiple customers from a single software instance and infrastructure. This approach offers distinct advantages:
1. Cost Efficiency
By sharing resources among multiple tenants, costs are distributed, making multi-tenancy a more affordable option. This model is particularly attractive for startups and small businesses looking to minimize IT expenses. The shared infrastructure allows SaaS providers to offer competitive pricing without compromising on quality.
2. Scalability
Multi-tenancy excels in scalability. As your business grows, the SaaS provider can effortlessly scale the infrastructure to accommodate more users without significant additional costs. This scalability ensures that your software can grow alongside your business, handling increased demand with ease.
3. Simplified Maintenance and Upgrades
In a multi-tenant setup, the SaaS provider manages all maintenance tasks, including updates and patches. This "hands-free" approach allows your team to focus on core business activities rather than worrying about IT maintenance, ensuring that you always have access to the latest features and security enhancements.
4. Efficient Resource Utilization
Sharing resources leads to optimal utilization, reducing waste and maximizing the efficiency of the underlying infrastructure. This efficiency not only lowers operational costs but also enhances the overall performance of the SaaS application.
Despite these benefits, multi-tenancy has its own set of challenges:
Choosing between single-tenant and multi-tenant architectures depends on your specific business needs, industry requirements, and budget constraints.
Understanding the cost dynamics of each architecture is crucial for making an informed decision.
Security is a top priority for any business adopting cloud solutions. Both architectures offer robust security features, but they handle risks differently.
As businesses seek the best of both worlds, a mixed tenancy model is gaining traction. This approach combines the isolation of single-tenancy with the cost-efficiency of multi-tenancy. For example, sensitive processes can run on dedicated instances while less critical components share a common infrastructure.
Security is a non-negotiable aspect of cloud computing. Whether you choose single-tenancy or multi-tenancy, implementing robust security measures is essential.
Choosing between single-tenant and multi-tenant architectures isn’t a one-size-fits-all decision. It hinges on your specific business needs, industry requirements, and budget constraints. Here’s a quick recap to guide your decision:
In cloud computing, making the right architectural choice is crucial for your business’s success. Whether you lean towards single-tenancy for its robust security and customization or multi-tenancy for its cost efficiency and scalability, understanding the implications of each model empowers you to make informed decisions.
At Prioxis, we understand the intricacies of both architectures. Our expertise lies in helping businesses like yours navigate these choices, ensuring that your cloud strategy aligns with your operational goals and security requirements. Whether you’re a startup aiming to scale efficiently or an enterprise seeking enhanced data protection, we’re here to guide you every step of the way.
Get in touch