Expertise
Smooth integration of information is required for quality operation and patient care in the current digital healthcare landscape. From 2013 to 2020, the health data amount grew exponentially, from 153 exabytes to 2,314 exabytes. Effective management and utilization of this huge data volume rank among the main challenges.
By combining patient information, billing, R&D, and pharmacy data, healthcare providers can offer real-time access, enhanced decision-making, and enhanced patient care. Interoperability issues, cost, and security concerns normally deter smooth integration.
This handbook discusses the issues, healthcare software solutions, and emerging technologies that are revolutionizing healthcare data integration and its implications for the healthcare industry.
What is Data Integration in Healthcare?
Healthcare data integration refers to combining data from varied sources into one comprehensive, up-to-date, and usable system. It dissipates data silos, and healthcare providers gain a single source of truth (SSOT) on which to base decisions.
Data integration will only be successful if the data is transformed and cleansed to provide consistency, accuracy, and functionality across systems. Through enabling immediate communication between health systems, integration healthcare provides real-time access to patient data, efficient workflows, and improved delivery of care.
Data Integration Technologies for Healthcare Systems
Data integration technologies have revolutionized healthcare by allowing hassle-free data sharing and real-time analysis. These are four important technologies that are leading the integration of healthcare systems:
- Extract, Transform, Load (ETL)
ETL is the foundation of healthcare data integration, effectively processing large-scale batch and incremental updates. It makes sure data is cleansed, transformed, and loaded into one system that is analyzed and used for decision-making.
- Enterprise Information Integration (EII)
EII provides on-demand access to multiple sources of information, giving an up-to-the-minute business perspective without physical consolidation of data. It supports ease of querying, analysis, and reporting across platforms.
- Enterprise Data Replication (EDR)
EDR creates real-time replication of data from multiple sources into target systems without altering the native data. It is designed with high-speed data movement and ensures timely information between platforms.
- Data Visualization
Highly sophisticated analytics and reporting capabilities help healthcare professionals navigate intricate data through intuitive dashboards, reports, and charts. They facilitate instant insights for improved decision-making and patient care.
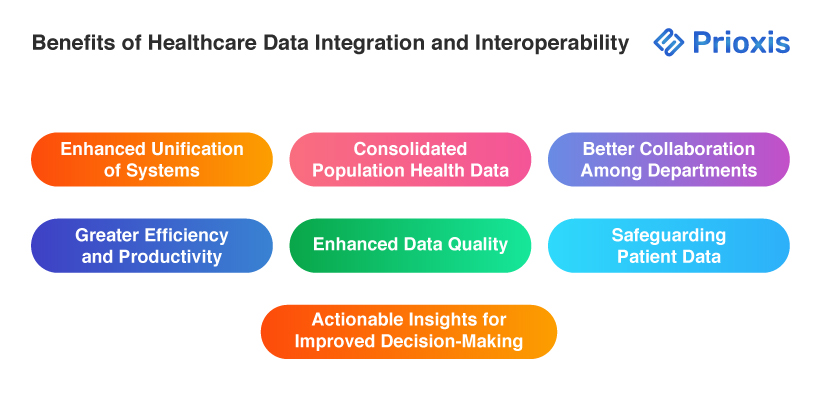
Benefits of Healthcare Data Integration and Interoperability
Healthcare data interoperability and integration provide essential benefits that greatly improve patient care and operational effectiveness. Some of the main advantages include:
- Enhanced Unification of Systems
Data integration provides a unified environment where information from different sources is consolidated. This unification makes it easier to transfer and access data, ensuring that patient data is easily accessible, whether gathered by healthcare providers or wearable devices.
- Consolidated Population Health Data
By combining data about disease incidence and health trends, healthcare professionals are able to easily track population health. This knowledge is crucial in disease management, public health campaigns, and outcomes improvement among vulnerable populations.
- Better Collaboration Among Departments
The care of the patient is done in collaboration between various departments. Data integration brings a smooth flow of information, which enhances collaboration and effectiveness in handling patients—admission through treatment and billing.
- Greater Efficiency and Productivity
Uninterrupted access to accurate patient information enables healthcare professionals to make timely decisions. This is efficient, minimizes redundancy, saves costs, and eventually enhances the ability to attend to more patients effectively.
- Enhanced Data Quality
Data aggregation removes errors and enhances accuracy. Quality and timely data are paramount for efficient patient care and management operations to support decisions based on reliable information.
- Actionable Insights for Improved Decision-Making
Integrated data enables healthcare professionals to derive valuable insights that inform enhanced patient care and support strategic decision-making in public health.
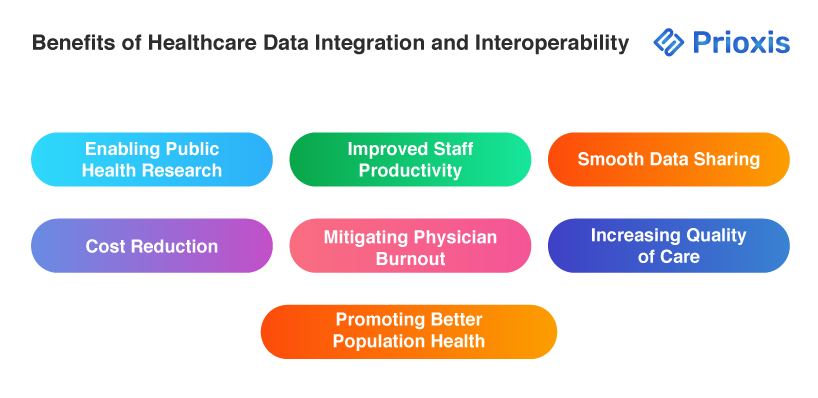
- Safeguarding Patient Data
Interoperability also enables data security by reducing manual data entry and enabling automated sharing. This reduces error to a minimal level and maintains sensitive information security through effective access controls and robust encryption methods.
- Enabling Public Health Research
Interoperability enables researchers to acquire standardized and uniform patient information for epidemiological studies and health evaluations, ultimately enhancing community health programs and public health outcomes.
- Improved Staff Productivity
Interoperable systems enable automated record entry and instant access to records, permitting healthcare providers to devote more time to patient care and less time to paperwork.
- Smooth Data Sharing
Interoperability enables timely sharing of patient information with external entities, such as insurance providers and other healthcare providers, resulting in improved coordination and continuity of care.
- Cost Reduction
With reduced administrative costs and the elimination of unnecessary tests, interoperability results in dramatic cost savings in healthcare operations, enabling care at lower costs to both providers and patients.
- Mitigating Physician Burnout
By reducing administrative tasks and enhancing access to patient data, interoperability allows medical professionals to maintain improved work-life balance, reduce stress, and enjoy greater job satisfaction.
- Increasing Quality of Care
Improved patient data access reduces medical errors and allows medical professionals to make fully informed decisions, resulting in enhanced treatment outcomes.
- Promoting Better Population Health
Through the analysis of aggregated patient information, healthcare organizations can detect health trends, reduce risk, and initiate targeted interventions that improve community health and close disparities.
Challenges Faced in Healthcare Data Integration
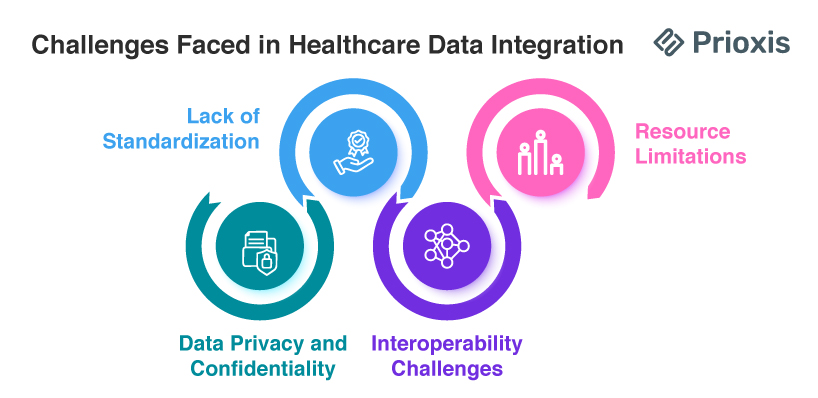
- Lack of Standardization
There is no standard data format and process for managing them, which is one of the biggest challenges in healthcare data integration. With an enormous amount of historical and real-time data, integrating it for easy access requires implementing uniform standards throughout the industry.
- Data Privacy and Confidentiality
Due to the fact that medical information is mostly personal and sensitive, elevated levels of security are essential. Compliance with rules such as HIPAA is a requirement in upholding individuals' privacy and protected storage of data to avoid unauthorized use and breaches.
- Interoperability Challenges
The majority of medical systems are not interoperable, and it is challenging to exchange data between different systems. Fragmentation causes partial or incomplete patient records, and this results in inefficiencies and compromises coordinated patient care.
- Resource Limitations
Healthcare organizations are often confronted with budget constraints and do not possess the requisite human and technological capabilities to successfully install integration solutions. This can hamper the effective implementation of integration programs.
Best Practices for Seamless Healthcare Data Integration
- Know Your Data
It is important to understand the kind of data that has to be gathered to integrate data in healthcare effectively. Organizations need to evaluate their data needs by raising important questions: Are healthcare professionals employing EHR/EMR systems that address their needs? What are the unmet needs of staff and patients? How are current systems being leveraged to improve care delivery and save costs? By answering these questions, organizations can improve their integration plans and make sure that they collect meaningful data in future deployments.
- Utilize Cloud-Native Architecture and APIs
Because of the wide and geographically distributed nature of medical data, embracing cloud-native architectures with API support is a must. It enables efficient data connectivity and allows real-time access to scattered patient data from disparate sources. A hybrid, cloud-native solution makes data integration more efficient.
- Train Your Team on FHIR Standards
Your software development team must be trained on Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resource (FHIR) standards for effective data integration. FHIR offers a standard framework for the organization of healthcare data, ensuring interoperability among various systems. Training on such standards prepares teams to implement effective data exchange practices while taking into account the distinctive complexities of healthcare data.
- Use Analytics Tools
Data connection to analytical solutions is imperative to realize secure and scalable health data integration. These solutions guarantee flawless connections between databases and help organizations design future growth and security solutions. Using analytics not only optimizes data usage but also facilitates decision-making in clinical environments.
- Authorize Data Access and Management
Effective healthcare data management demands structured access to information for decision-makers. Software vendors and providers need to set clear guidelines for providing the right data access to the right people, ensuring the right individuals have real-time information for effective communication and healthcare data management.
- Safeguard Your Data
Healthcare organizations need to be compliant with rigorous data privacy laws, including HIPAA, HITECH, and HL7. The implementation of strong security controls safeguards patient data and guarantees compliance with regulations, thus establishing trust and integrity in managing healthcare data.
Use Cases Of Healthcare Data Integration
Healthcare data integration has multiple applications that maximize the abilities of healthcare professionals and enhance patient care. Some of the key use cases include:
COVID-19 Pandemic Response:
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the value of integrated healthcare information in responding to disasters. Integrating data from many sources better enabled healthcare organizations to create well-informed patient care and crisis response plans.
The majority of health officials did not have integrated information, which only restricted them from making informed choices. With greater access to consolidated data, the decision-makers would have optimized immunization distribution, synchronized operations with frontline personnel, and minimized morbidity and mortality among patients throughout the outbreak.
Fraud Detection
Fraud has become an epidemic in the healthcare industry in the guise of identity theft, overcharging, and charging for services not delivered. Healthcare data integration can go a long way in detecting and preventing fraud.
By cross-matching billing records, patient information, and medical records, organizations can identify irregularities and discrepancies. AI and machine learning-based real-time monitoring, pattern analysis, and predictive modeling can also help detect fraud, and hence prevention and prosecution are feasible.
Population Health Management
Population health management relies on integrated healthcare data. It allows healthcare organizations to process big data, find patterns, and identify populations at risk.
For example, in the COVID-19 pandemic, integrated data helped intervene in patients showing symptoms early, and telehealth software services were adopted quickly. Through the identification of populations at risk, healthcare providers can intervene specifically, avoid redundant testing, and ultimately improve patient care.
Patient-360 View
Patient-360 view presents a holistic image of patient data by bringing together various sources of data, including EHR history, medical histories, insurance claims, laboratory data, and demographics. The 360-degree perspective allows healthcare workers to see patterns in patients' behaviors, make more accurate diagnoses, and devise tailored care plans.
Drug Discovery
Drug development is a complex process that benefits significantly from data integration. By facilitating access to diverse datasets, including clinical trial data integration results and scientific publications, healthcare data integration supports researchers in understanding drug efficacy and safety. This holistic view accelerates the research process and enhances the likelihood of successful drug discovery.
Crisis Response
Integrated healthcare information is crucial for informed decision-making in times of crisis, like natural calamities or health crises. With real-time data at their disposal, healthcare organizations can react promptly and efficiently, providing the best care to patients while also keeping frontline workers safe. Being agile is important in handling tough situations and ensuring top-quality care.
Wrapping Up
The history of data integration in healthcare has made it an essential part of patient management. With almost 96 percent of hospitals adopting Electronic Health Record (EHR) technology, providers now face a heterogeneous array of EHR systems, as many as 18 at times in a single system.
Real-time EHR Data Integration enhances Clinical Data Integration efficacy by consolidating disparate health data, allowing clinicians to identify gaps in care and make better-informed decisions. Cloud computing also democratizes access to advanced integration technologies, allowing even the smallest healthcare providers to realize unity of data.
Ultimately, healthcare data integration produces a more empathetic and responsive model of patient care, improving outcomes and operations. As the industry continues to advance, focus on data-driven care will be essential to shaping the future of healthcare delivery.