Expertise
It's the backbone of modern business operations. ERP solutions are designed to improve and streamline various processes across different departments within an organization.
Whether it's finance, human resources, supply chain, or manufacturing, ERP ensures that every aspect of a business works in harmony.
What is ERP?
At its core, ERP is a system of integrated software solutions that bring together various business functions. It provides a centralized platform for managing operations like sales, delivery, accounting, supply chain, and distribution. By connecting these diverse functions, ERP enhances communication and coordination between departments, ensuring they work in sync.
The Purpose of ERP Software Development
The primary goal of ERP is to boost productivity by making administrative processes more efficient and reducing the costs associated with resource planning. This is achieved by integrating various business operations into a single, unified system. Most ERP systems today are implemented as either mobile or web-based software, offering flexibility and accessibility.
ERP Modules and Their Functions
ERP systems consist of many modules, each designed to manage specific business functions. These modules are connected to a common database, allowing them to work independently or together as needed.
This modular approach makes ERP systems customizable, enabling businesses to include or exclude modules based on their unique requirements.
Here are the essential modules found in an ERP Software Development:
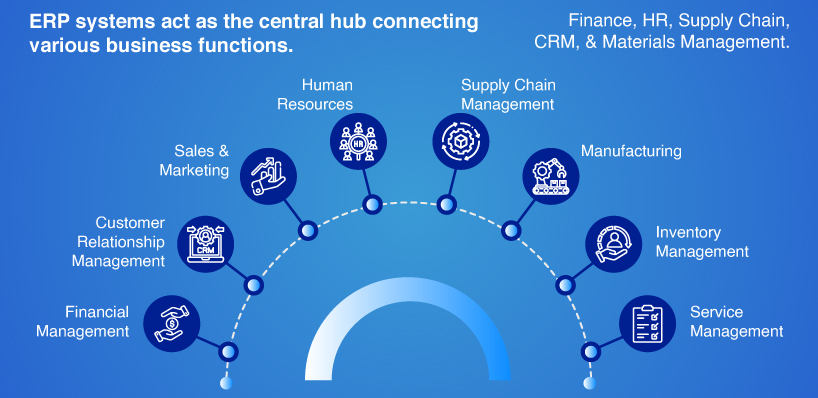
Financial Management
This module oversees financial operations, tracks transactions, controls budgets, reduces expenses, and ensures right accountability.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM solutions within ERP Software Development manage client databases, analyze customer demand, find market trends, and help build effective marketing strategies.
Sales & Marketing
This module handles sales processes such as inquiries, orders, quotations, and invoices. It often works closely with the CRM module to enhance marketing efforts and increase profitability.
Human Resources (HR)
The HR module manages all aspects of employee management, from hiring to payroll to dismissal procedures. It often integrates with the financial module for payroll processing.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
SCM tracks demand, resources, production status, logistics, and distribution. It improves supply and resource management to keep the company competitive.
Manufacturing
This module oversees production processes, from product planning to quality control and forecasting, ensuring efficient and prompt manufacturing operations.
Inventory Management
This part provides correct inventory reports and manages delivery processes, logistics, and document flow, often in collaboration with other modules.
Service Management
Working alongside the CRM module, this part focuses on enhancing customer service by tracking orders, inquiries, and service quality.
Market Trends in ERP Software Development
The ERP market has seen significant growth, driven by the demand for operational efficiency and transparency. Despite the costs associated with ERP development, the benefits are clear.
Over 53% of companies consider ERP a priority investment, with 95% of users reporting improved workflows. As digital transformation continues, the ERP industry is expected to grow at an average rate of 11.0% from 2023 to 2030.
Cloud-based ERP solutions are particularly on the rise. The market projected to grow from $45.3 billion in 2020 to a compound annual growth rate of 17.4% by 2025.
Small and mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly adopting cloud ERP, which could account for up to 40% of this market by 2025.Modules of ERP
Why Do You Need ERP System Development?
1. Streamlined Processes
ERP systems streamline workflows by cutting redundant tasks, leading to increased operational efficiency. This not only boosts productivity but also ensures that business processes run smoothly and without unnecessary delays.
2. Centralized Data Integration
With ERP, all your business data is centralized into a single platform, creating a "single source of truth." This integration fosters better collaboration across departments and enables more accurate and informed decision-making.
3. Enhanced Visibility
ERP Software Development offers real-time insights into key metrics and performance indicators, giving businesses the visibility they need to make informed decisions. This visibility allows companies to quickly adapt to changing market conditions, staying ahead of the competition.
4. Improved Compliance
ERP systems help businesses support regulatory compliance by enforcing standardized processes. They facilitate right reporting and auditing, ensuring that your business stays on the right side of industry regulations.
5. Scalability
As your business expands, your ERP system grows with you. ERP software is designed to scale seamlessly, accommodating your changing needs without requiring a complete overhaul. This scalability ensures that your investment in ERP continues to provide value over time.
6. Data-Driven Insights
ERP combines information from various sources, offering valuable data-driven insights. This centralized data platform enables businesses to find trends, patterns, and opportunities, laying the groundwork for strategic planning and quick adaptation to market changes.
7. Increased Productivity
By automating manual processes and tasks, Custom ERP Software Development save time and reduces errors. Employees can focus on more meaningful work, increasing overall efficiency and contributing to higher profitability.
8. Improved Collaboration
ERP unifies enterprise-related information, reducing communication delays across departments or branches. This improved collaboration is especially valuable for businesses with a wide-reaching network, whether across multiple states or continents.
9. Faster Decision-Making
With real-time data access and user-friendly reporting tools, Custom ERP Software Development empowers businesses to make faster, more informed decisions. This ability to quickly assess the efficiency of workflows and costs helps companies respond more effectively to challenges.
10. Better Customer Service
ERP systems centralize client and sales-related information, making it easier for sales managers and customer service teams to provide excellent service. By accessing customer histories and analyzing behavior patterns, companies can forecast demand accurately and meet customer needs more effectively.
11. Built-In Compliance
Staying compliant with industry regulations is crucial, and ERP Software Development help businesses keep up with changes in compliance rules and guidelines. This built-in compliance feature ensures that your business stays up-to-date and avoids potential regulatory pitfalls.
12. Resource Optimization
ERP revolutionizes resource management by providing greater visibility into inventory levels, procurement processes, and supply chain activities. This leads to optimized resource allocation, reduced inventory carrying costs, and improved supplier negotiations, all of which contribute to better financial performance.
13. Flexibility and Scalability
ERP software is highly adaptable, allowing businesses to scale operations up or down as needed. Whether you're expanding production, adding new services, or increasing inventory, ERP systems can adjust to meet your evolving business requirements.
14. Increased Information Access
Advanced ERP systems centralize the collection, processing, and storage of customer and product-related data. This cuts redundant information and ensures that all data is up-to-date, enhancing performance across the organization, particularly in supply chain management and inventory control.
15. Comprehensive Reporting
ERP software simplifies reporting by centralizing data into one easily accessible location. Whether you need financial, customer behavior, or maintenance reports, ERP systems make it easy to generate and share them across departments, fostering better communication and decision-making.
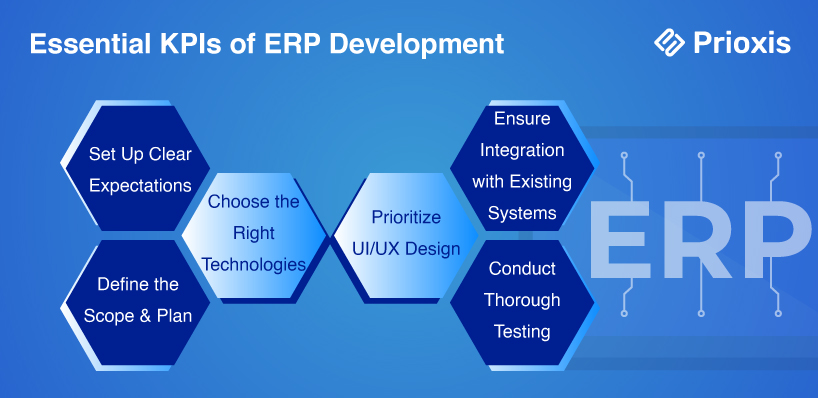
Essential KPIs of Custom ERP Software Development
When embarking on ERP development, it's crucial to keep certain Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in mind to ensure the project's success. Here’s a breakdown of what you should focus on:
1. Set Up Clear Expectations
Before diving into custom ERP development, it’s essential to set clear, realistic expectations. This involves defining what you want the system to achieve and ensuring that all stakeholders and developers are on the same page. By doing this, you set the stage for a smoother collaboration and a more successful project outcome.
2. Define the Scope and Plan
After setting up your expectations, it's time to outline the project's scope. This includes deciding on the type of ERP implementation and creating a general project plan. The plan should cover the system's basic modules, the composition of the development team, needed resources, an estimated budget, and a timeline with key milestones. This roadmap will help keep the project on track and within budget.
3. Choose the Right Technologies
Selecting the right technology stack is vital for the success of your ERP system. The three main technological aspects to consider are system hosting, the programming framework, and database implementation.
Your choice of hosting—whether local or cloud-based—will influence the level of maintenance required post-implementation. The programming framework, often chosen by the development team, includes widely-used options like JavaScript for both frontend and backend development.
For databases, the choice between SQL (relational) and NoSQL (non-relational) depends on your company's size and the variety of data you manage.
4. Focus on UI/UX Design
A user-friendly interface is crucial for the efficiency of your ERP solution. Focus on designing a simple and intuitive UI/UX that makes all necessary tools easily accessible. A well-designed interface ensures a positive user experience, which is essential for the system's adoption and effectiveness.
5. Ensure Integration with Existing Systems
Most organizations already have existing databases and specialized applications. Before starting the development process, it’s important to integrate these existing systems with the new ERP solution. This consolidation helps ensure a smooth transition and continuous operation without the need for more integration tools later on.
6. Conduct Thorough Testing
Testing is a critical phase in ERP development. It helps find and correct discrepancies before the system goes live. During testing, it’s important to verify that the final product meets the first requirements, functions correctly, and is secure. Involving focus groups from key departments in the testing process can provide valuable feedback and ensure the system meets user needs.
Must-Have Features for Custom ERP Software Development
1. Flexible Hosting Options
Every business has unique security and flexibility requirements. A robust ERP system should offer many hosting options, including on-premises servers, cloud storage, and hybrid platforms. This flexibility allows businesses to choose the solution that best fits their needs, whether they focus on data protection, accessibility, or cost-efficiency.
2. Easy Integration
ERP systems are modular, meaning they encompass various business functions like CRM, CMS, Supply Chain Management, Finance, HR, and more. For the system to be effective, it must integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure and other software solutions. This integration prevents operational silos and ensures a cohesive workflow across all departments.
3. Business Process Automation
Automation is a cornerstone of ERP systems. By automating routine tasks such as order entry, billing, payroll, and reporting, ERP solutions significantly increase productivity. Automation reduces the time and resources spent on manual processes, minimizes errors, and allows employees to focus on more strategic activities.
4. Scalability
An effective ERP system must be scalable to accommodate the evolving needs of a growing business. Scalability ensures that the system stays relevant and efficient as the company expands, preventing the need for costly overhauls or the addition of cumbersome applications.
5. Mobile Compatibility
In today’s mobile-first world, ERP systems must be accessible from any device—whether it’s a smartphone, tablet, or laptop. Mobile compatibility ensures that teams can work efficiently from anywhere, enhancing productivity and enabling real-time decision-making, regardless of location.
6. Accurate and Automated Reporting
Automated reporting is essential for keeping time-efficient workflows. ERP systems generate reports automatically, reducing the need for manual intervention. These reports, which can include custom dashboards, bar graphs, pie charts, and Gantt charts, offer valuable insights and support informed decision-making.
7. Transparent Tracking
Transparency in tracking is crucial for effective resource management. A well-integrated ERP system provides tools to track both tangible and intangible data across the organization. This feature is particularly useful for monitoring inventory, customer information, and employee performance, ensuring that all aspects of the business are under control.
8. Global Integration
For businesses running across multiple locations or departments, global integration is a key feature. ERP systems should ease high-level synchronization between different branches, allowing them to work together seamlessly. This integration promotes a well-coordinated workflow and ensures that all parts of the business are aligned.
9. Real-Time Operations
Real-time data access is vital for efficient operations. ERP systems should support real-time processing and updates, ensuring that all users have immediate access to the latest information. This feature streamlines workflows and enables quick, informed decision-making.
10. Common Database
A common database is fundamental to the smooth operation of any ERP system. It ensures that all information entered into the system is stored centrally and is accessible by authorized users across different departments. This centralization reduces data redundancy and enhances collaboration.
11. Advanced Data Analytics
Data analytics is another critical feature of ERP systems. By analyzing collected data, the system can find trends, predict future performance, and offer actionable insights. This analytical capability makes the ERP system more effective and helps businesses reduce costs by optimizing processes.
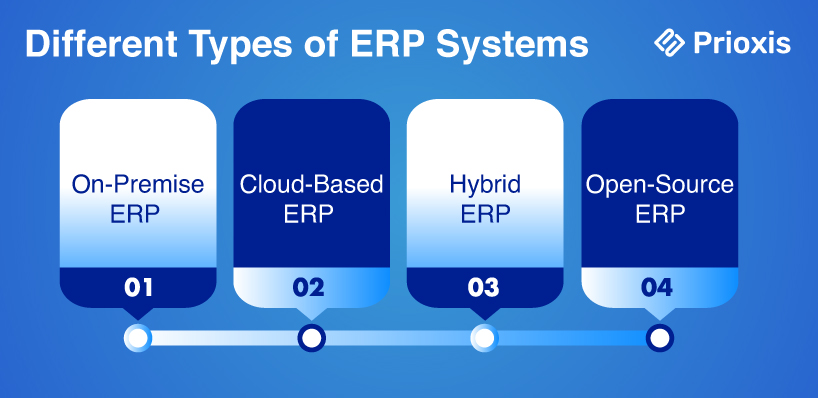
Different Types of ERP Systems
1. On-Premises ERP
On-premises ERP systems are installed locally on your company’s servers and managed by your internal IT team. This type of ERP gives you complete control over the system, including data security, customization, and integration.
Advantages of On-Premises ERP
- Complete Control You have full oversight of your ERP system's security and performance.
- Customization ERP modules can be tailored specifically to the unique needs of your business.
- Seamless Integration Easily integrates with other internal systems without third-party involvement.
- Data Security Sensitive information stays within your organization, reducing risks associated with external data handling.
2. Cloud-Based ERP
Cloud-based ERP is also known as Software as a Service (SaaS). This ERP Development Services is hosted on the vendor’s servers and accessed via the internet. This type of ERP is managed by third-party providers, allowing your team to access it from any device with internet connectivity.
Advantages of Cloud-Based ERP
- Cost-Effective Lower upfront costs as there's no need for expensive hardware or extensive IT staff.
- Accessibility Access your ERP system from anywhere, on any device, making it ideal for remote work.
- Ease of Use Generally, requires less technical ability to install and maintain.
- Scalability Easily scalable to meet growing business needs without significant investment.
Explore Further: On Premises vs Cloud
3. Hybrid ERP
Hybrid ERP, sometimes referred to as two-tiered ERP, combines the strengths of both on-premises and cloud-based systems. This ERP Development Services allows companies to use both solutions simultaneously, meeting specific business needs while maintaining flexibility.
Advantages of Hybrid ERP
- Best of Both Worlds Uses the control and customization of on-premises ERP with the accessibility and scalability of cloud-based ERP.
- Flexibility Choose which functions to keep on-premises and which to host in the cloud, balancing security and accessibility.
- Cost Efficiency Potentially lower costs by optimizing which parts of the system are hosted and were.
4. Open-Source ERP
Open-source ERP systems offer a more budget-friendly option by providing the software for free, with users typically paying only for cloud hosting or other services. These systems require more hands-on management, as the responsibility for setup, customization, and maintenance often falls on the user.
Advantages of Open-Source ERP
- Affordable Low or no upfront software costs make it accessible for smaller businesses or startups.
- Customizable High level of flexibility in terms of system configuration and customization.
- Community Support Often supported by a community of developers, which can be a valuable resource for troubleshooting and improvements.
- No Vendor Lock-In Freedom to change the source code as needed, without relying on a single vendor.
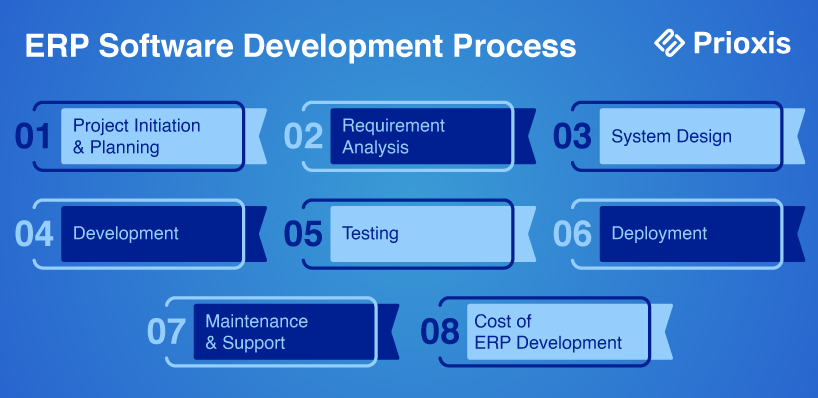
ERP Software Development Process
1. Project Initiation and Planning
The first stage in ERP development is defining the project's scope, goals, and requirements. This involves close collaboration with stakeholders from various departments to ensure that the ERP system will meet the organization's needs.
The project team conducts feasibility studies and risk assessments to find potential challenges and opportunities. A detailed project plan is then created, outlining timelines, resource allocation, and key deliverables.
2. Requirement Analysis
In this stage, detailed requirements are gathered from stakeholders across all relevant departments, such as finance, HR, manufacturing, and more. These requirements are meticulously documented, distinguishing between functional needs (what the system should do) and non-functional needs (like performance, scalability, and security).
Prioritizing these requirements based on business needs and feasibility is crucial for guiding the development process effectively.
3. System Design
Designing the architecture of the ERP system is a critical step that ensures scalability, security, and seamless integration with existing systems.
This stage involves developing data models to define the database structure and the relationships between different data entities. Additionally, user interfaces (UI) for different modules and roles within the ERP system are designed to ensure usability and efficiency.
A comprehensive technical design document is created, outlining the system’s components, technologies, and their interactions.
4. Development
With the design in place, the actual development of the ERP system begins. This involves implementing the system’s functionality according to the defined requirements. Developers work on creating modules for various functional areas such as finance, HR, inventory management, and accounting.
The choice of programming languages, frameworks, and development tools is critical for building a robust and scalable system. Often, Agile methodologies are employed to ease iterative development, allowing for flexibility and continuous improvement throughout the process.
5. Testing
Testing is a crucial phase in the ERP development process. It ensures that the system is reliable, functional, and meets the organization's requirements. Various types of testing are conducted, including unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT).
These tests are designed to find and fix any bugs, errors, or performance issues. Validation against real-world scenarios and workflows is essential to confirm that the system will function correctly once deployed.
6. Deployment
Deployment involves rolling out the ERP system to end-users. This stage includes planning and executing the strategy for data migration, system configuration, and user training.
The goal is to minimize downtime and disruption to business operations. Post-deployment testing is conducted to verify the system's performance in a live environment. Additionally, support and training are provided to ensure that users can effectively run the new system.
7. Maintenance and Support
After deployment, ongoing maintenance and support are vital for the continued success of the ERP system. This includes addressing issues such as bug fixes, security patches, and system updates.
Continuous monitoring of system performance and user feedback helps in finding areas for improvement. Technical support is provided to help users and administrators in resolving issues promptly. Regular evaluations and updates are necessary to adapt the ERP system to evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Cost of ERP Development
The cost of developing an ERP system can vary. The cost includes several factors such as requirements analysis, design, development, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance. Extra costs might include infrastructure setup, user training, and integration with existing systems.
Factors Influencing Cost
- Development Team The experience and location of your development team significantly affect costs. Experienced developers may command higher fees, but they often deliver higher-quality work more efficiently.
- Development Hours The complexity of the ERP system and the time needed to develop it directly affect costs. More complex features require more development time and resources.
- Location of Developers Geographic location plays a significant role in pricing. For example, development costs in North America are generally higher compared to regions like India, where services may be more affordable without compromising quality.
Core Criteria for Choosing an ERP Software Development Company
Selecting the right ERP development company is crucial to the success of your project. Here are key criteria to consider:
- Expertise Look for a company with at least five years of experience in software development, particularly in ERP projects or related fields like inventory management.
- Technical Knowledge Ensure the company has a strong understanding of the software development process and the specific tech stack that aligns with your project needs.
- Industry Experience A company with experience in your industry, whether it’s manufacturing, finance, or another sector, will better understand your specific requirements
Why Choose Prioxis as Your ERP Software Development Company?
Prioxis stands out as the trusted ERP Development Company. Here's why:
Proven Expertise
With over five years of experience in ERP and software development, our ERP Software Development Services bring deep technical knowledge to your project.
Industry-Specific Solutions
We understand the unique challenges of various industries, allowing us to tailor ERP solutions that align with your business needs.
Comprehensive Support
From first consultation to ongoing maintenance, our ERP Software Development Services offers end-to-end services that ensure your ERP system is efficient, secure, and future-proof.
Challenges to Consider When Building a Custom ERP Solution
Developing a custom ERP solution can be a transformative process for your business, but it comes with its share of challenges. Here are some key obstacles to keep in mind as you navigate this complex undertaking:

1. Balancing Customization with Maintainability and Future-Proofing
One of the biggest challenges in building a custom ERP system is striking the right balance between customization and maintainability. While customization allows the ERP to meet the specific needs of your business, excessive modifications can lead to a system that is overly complex and difficult to maintain.
To address this, consider adopting a modular design that allows for easier updates and maintenance. Use industry-standard technologies to ensure that your system stays compatible with future advancements.
Carefully manage customization requests, prioritizing those that offer the most value while minimizing potential impacts on the system's long-term sustainability.
2. Avoiding Scope Creep and Managing Project Timelines
Scope creep, where more requirements are continuously added to the project, is a common issue in custom ERP development. This can lead to delays, budget overruns, and a final product that is more complex than initially intended.
To avoid this, set up clear project requirements from the outset and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned with these goals. Implement a strict change management process to evaluate and approve any changes based on their impact on the project timeline and budget. Regularly review the project’s progress against the original plan to keep it on track.
3. Mitigating Risks Related to Compliance, Security, and Data Privacy
Compliance with industry regulations and data privacy laws is non-negotiable when developing a custom ERP system. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in significant fines, legal issues, and damage to your company’s reputation.
To mitigate these risks, implement robust security measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Ensure that your ERP system follows relevant regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, or any other applicable laws. Regular assessments should be conducted to confirm that the system stays compliant over time, adapting to any changes in the regulatory landscape.
Conclusion
Building a custom ERP solution is a complex and challenging process, but with careful planning and consideration of these key challenges, it can lead to significant benefits for your organization.
Balancing customization with maintainability, managing scope creep, and ensuring compliance and security are all critical to the success of your ERP project.
With our ERP Software Development Services, you can navigate these challenges and build a custom ERP system that drives long-term success for your business.