Expertise
Telemedicine is fast, convenient, and designed to fit around your life. Need advice on a mild issue? A follow-up for a chronic condition? Or just a quick check-in? With telemedicine, it’s as simple as making a video call or sending a message.
It is mostly used for managing ongoing conditions, telemedicine can also involve remote monitoring tools. These devices send your health updates directly to your doctor, who can keep an eye on things and adjust as needed without scheduling a visit. Even prescriptions are simplified. After your appointment, your doctor can send prescribed medicines straight to your pharmacy so you can pick them up at your convenience.
Telemedicine brings healthcare to you compared to the traditional healthcare system, making it flexible, accessible, and built to keep up with the pace of everyday life.
What is Telemedicine?
In simple terms - Telemedicine is healthcare right at your fingertips. Instead of going to a clinic and waiting to see a doctor, you can talk to a medical professional directly through your phone or tablet whether you're at home, at work, or even traveling.
Challenges Faced in Traditional Healthcare Systems
Traditional healthcare systems face a range of challenges that impact patient experience, provider efficiency, and operational costs. Here are some of the key challenges:
Accessibility and Convenience
Many patients face difficulties accessing timely medical care due to location, limited transportation, or mobility issues. Rural and underserved communities, in particular, often lack nearby healthcare facilities, making it harder to reach essential services.
Long Wait Times
Long waiting periods for appointments and in-clinic delays are common, which can lead to patient dissatisfaction, delayed diagnoses, and unnecessary strain on healthcare facilities. This challenge often discourages patients from seeking care early, impacting health outcomes.
High Operational Costs
Running a traditional healthcare facility requires significant investment in infrastructure, staffing, and medical equipment. The high operational costs make it challenging to maintain affordable care for patients, especially in high-demand areas.
Limited Resources and Workforce Shortages
Healthcare facilities frequently experience shortages of qualified medical staff, especially in specialized fields. This leads to provider burnout, increased workloads, and difficulty in delivering high-quality patient care.
Fragmented Patient Data
Patient data is often stored in separate systems, making it challenging for providers to access comprehensive health records during consultations. This fragmentation can lead to errors in treatment, duplicative tests, and difficulty in creating personalized care plans.
Increased Pressure on Emergency Services
Many patients visit emergency departments for non-emergency conditions due to a lack of access to primary care or after-hours support. This strains emergency resources, leading to overcrowded ERs and potentially delaying care for critical cases.
Inefficient Processes and Paperwork
Administrative tasks, like handling insurance claims and patient records, take up a significant portion of healthcare providers’ time. Paper-based or outdated electronic systems slow down workflows, reduce time available for patient care, and increase the likelihood of administrative errors.
Inconsistent Quality of Care
Due to differences in provider experience, availability of resources, and regional disparities, patients might receive inconsistent care across facilities. This inconsistency can negatively impact treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Lack of Patient Engagement and Education
Traditional systems often lack effective communication tools to keep patients engaged in their own healthcare journeys. Without resources or reminders, patients may not fully understand their treatment plans, follow-up needs, or preventive health measures.
Data Privacy and Security Risks
Protecting patient data is a significant challenge in traditional healthcare settings, especially with growing cybersecurity threats. Managing patient privacy under strict regulations like HIPAA adds complexity to data handling and technology usage within healthcare facilities.
Addressing these challenges requires modernization of healthcare practices, improved technology integration, and innovative solutions like telemedicine and digital health platforms. These approaches can optimize access, streamline processes, and enhance patient outcomes while reducing the load on traditional healthcare infrastructures.
How Does Telemedicine Address Traditional Healthcare Challenges?
Connect with a Doctor from Anywhere
You set up an appointment, and at the scheduled time, you talk to the doctor through your device (like a smartphone or computer). This makes it easier to get medical help from home, especially if you're in a remote area or have trouble traveling.
Convenient Care for Minor Issues and Follow-Ups
Telemedicine is ideal for non-emergency needs like discussing symptoms, managing chronic conditions, or getting guidance on ongoing treatments. After the call, if necessary, the doctor can send a prescription directly to a nearby pharmacy, simplifying the patient’s experience.
Tools for Monitoring Health
For clients managing ongoing health conditions, telemedicine can support continuous monitoring using at-home devices (e.g., blood pressure monitors or glucose meters). These devices send health data directly to the physician, helping doctors make proactive adjustments to care plans and improvising overall patient outcomes.
Top Use Cases of AI in Telemedicine
Spotting Health Issues Faster with AI Algorithms
AI-driven algorithms analyze patient histories, symptom patterns, and medical images like X-rays or CT scans to catch potential health issues early. By comparing against vast medical datasets, AI supports accurate, timely diagnoses that improve patient outcomes.
Prioritizing Urgent Cases with Natural Language Processing (NLP)
AI uses NLP to assess patient-reported symptoms, automatically identifying those who need immediate attention. AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots gather symptom information and use NLP to interpret responses, ensuring urgent cases are escalated to healthcare professionals quickly. Imagine the time and resource savings with this technology!
Continuous Monitoring for Chronic Conditions with Wearable Integration
For patients managing long-term health issues, AI uses real-time data from wearable devices to track vital signs—like heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels—alerting healthcare providers to any critical changes. Predictive analytics embedded in these devices ensure that chronic conditions are proactively managed.
Round-the-Clock Support with Virtual Health Assistants
AI chatbots, powered by machine learning, offer 24/7 patient support by answering common health questions, providing basic advice, and even scheduling appointments during the odd hours. This technology streamlines patient engagement and reduces administrative load.
Predicting Health Risks with Predictive Modeling and Data Analytics
AI's predictive analytics examine historical and real-time patient data to identify patterns that indicate potential health risks, giving healthcare providers a heads-up before conditions worsen. This predictive capability can help reduce emergency situations and focus on preventive care.
Medication Management with Machine Learning Reminders
AI-based tools send personalized reminders, track adherence, and monitor potential drug interactions, supporting patients in following their treatment plans. Through machine learning, these systems can adapt to individual patient needs, minimizing risks associated with missed or incorrect dosages.
Custom Rehab Plans Using Computer Vision and Progress Tracking
Using computer vision technology, AI applications can offer personalized rehabilitation exercises, monitor patient progress remotely, and provide feedback based on real-time movements. This technology turns at-home recovery into a guided experience with measurable outcomes.
Streamlining Clinical Documentation with Voice Recognition
AI-powered voice recognition transcribes conversations during telemedicine sessions and automatically structures notes for electronic health records (EHRs). NLP organizes and highlights key patient details, reducing paperwork and allowing healthcare providers to focus more on direct patient care.
Optimizing Telemedicine with Generative AI in Telehealth
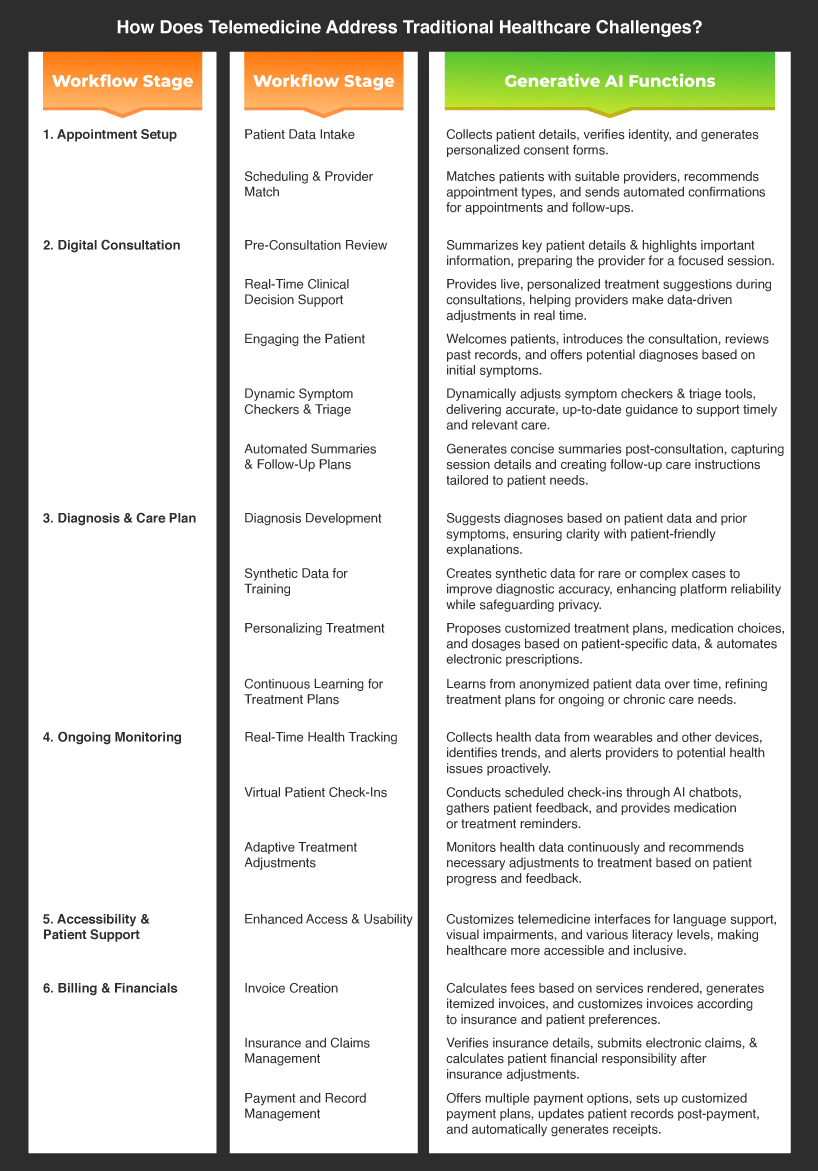
Real-Time Clinical Decision Support
Generative AI empowers physicians in telemedicine with instant, personalized insights. During live consultations, it suggests treatment adjustments based on real-time patient data, enabling providers to make tailored, timely decisions that enhance patient care.
Automated Patient Summaries and Follow-Up Plans
With generative AI, providers can skip manual notes. AI-generated summaries capture key details from each session, and personalized follow-up plans keep patients on track—allowing healthcare teams to focus more on care and less on admin.
Synthetic Data for Training and Research
Generative AI can create synthetic patient data for training, especially on rare or complex cases. This enhances diagnostic accuracy in telemedicine while preserving patient privacy, making platforms more reliable in varied medical scenarios.
Dynamic Symptom Checkers and Triage Support
AI-powered symptom checkers adapt dynamically, integrating the latest medical data for precise triage. This helps patients get faster, more accurate guidance, streamlining the telemedicine experience for better outcomes.
Continuous Learning for Personalized Treatment
Generative AI learns from anonymized patient data, refining long-term treatment plans for chronic conditions. For patients with ongoing needs, this means a proactive, personalized approach to evolving care
Enhanced Language Processing for Accessibility
AI enhances telemedicine accessibility by creating interfaces for diverse needs—translating instructions, adapting for visual impairments, or simplifying text for all literacy levels, making healthcare more inclusive.
Implementing AI in Telemedicine
Infrastructure Requirements
Implementing AI in telemedicine starts with a strong infrastructure. This involves using cloud platforms for fast, scalable data processing, secure data storage to keep patient info protected, and seamless integration with telehealth systems to support real-time AI insights. These components work together to deliver reliable, uninterrupted service during patient consultations.
Data Integration and Management
AI in telemedicine works best when platforms integrate seamlessly with existing systems like EHRs and patient portals. With secure encryption and strict compliance with privacy laws like HIPAA, this setup keeps patient data safe while enhancing AI’s ability to support doctors in decision-making.
AI Model Training and Testing
AI models perform best when they’re trained on a wide range of healthcare data. Regular testing and updates ensure that the AI stays accurate across different medical scenarios, from routine check-ups to complex cases. This process helps make sure that AI recommendations remain precise and clinically useful.
User Experience and Interface Design
A straightforward, intuitive interface is essential for successful AI adoption. Both patients and providers benefit from an intuitive, interactive and functional design that simplifies navigation. A well-designed interface makes sure the app is easy to use and accessible, no matter the user’s technical comfort level.
Compliance and Ethical Standards
Strict compliance with healthcare regulations and ethical standards is essential when implementing AI in telemedicine. This includes encrypting patient data, performing regular security checks, and ensuring transparency in data use. By meeting these standards, telemedicine providers can use AI responsibly while maintaining patient trust and safety.
Bringing Healthcare Closer with AI and Telemedicine
The future of healthcare is already here. By combining the human touch of medicine with AI's capabilities, we're not just making healthcare more convenient, we're making it more human with AI’s advanced analytics. With Artificial intelligence telehealth, Patients get the personalized attention they deserve, while doctors gain powerful tools to provide better care. It's a transformation that's making quality healthcare accessible to more people, right when they need it most.
The path to implementing AI-powered telemedicine is clearer than ever. With systems designed for seamless integration and compliance built-in from the ground up, healthcare providers can confidently take this step forward.
If you’re ready to explore what AI can do for your healthcare services, we’d love to help make it a reality. Let’s chat about how AI in healthcare can support your team and the people you care for.