In the modern corporate environment, effective project management is important in meeting and satisfying customer expectations and delivering high-quality deliverables. Project managers must decide on the delivery methodology to use when approaching a new project, program, or product.
Agile and waterfall are the two project management methodologies, but these methods also have their risks and rewards. As a project manager, you should pick the right approach according to your team's needs and the nature of your project.
However, flexibility is important regardless of the methodology so you can respond to any change in work circumstances. This blog will give an overview of the similarities and differences between agile and waterfall project management and what each has in store to get effective results.

What Is the Waterfall Model?
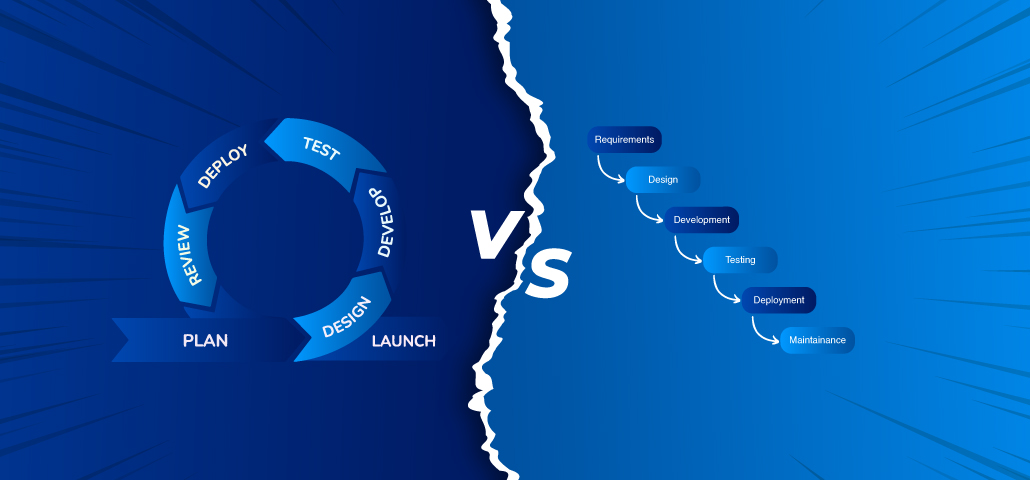
The waterfall model is one of the earliest and most straightforward methodologies applied in custom software development. This is a sequential design process usually applied in software development, whereby the progress flows steadily downwards like a waterfall through diverse phases.
The model is very structured, dividing the whole process of software development into different phases, each having its deliverable and review processes.
Pros and Cons of the Waterfall Approach
Waterfall software project management has its own set of advantages and disadvantages to consider when selecting the right software development methodology for your projects.
Pros of the Waterfall Model
- Clarity: Each phase has precise deliverables and a review mechanism, making it simple to understand and apply.
- Defined Stages: Clear, structured stages facilitate straightforward management and meticulous planning.
- Documentation: Comprehensive documentation provides a clear record of all project aspects.
- Minimal Scope Creep: Defined stages and requirements reduce the risk of project scope expansion.
Cons of the Waterfall Model
- Inflexibility: Once a stage is complete, backtracking or making modifications is difficult and expensive.
- Delayed Testing: Testing is typically performed after the build phase, potentially delaying issue identification.
- Resource Intensive: This may require more resources, especially if changes are needed after progressing beyond the initial stages.
- Lengthy Timelines: The structured nature might extend the project duration before producing any working model.
What Is The Agile Model?
The Agile Model is a highly adaptable and interactive method of software development that prioritizes adaptability, customer happiness, and incremental progress. Unlike traditional models such as Waterfall, which regard software development as a series of clearly defined phases, Agile views custom software development as short, controllable increments known as sprints or iterations.
The Agile Model is more than simply a set of software development processes; it is a mindset defined by the Agile Manifesto's ideals, which prioritize persons and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and adapting to change.
Pros and Cons of the Agile Approach
Agile project management isn't all smooth sailing; it comes with its own set of advantages and challenges that you'll need to consider.
Pros of the Agile Model
- Adaptability: Easily adapts to changes, even late in the development process.
- Feedback: Continuous customer and stakeholder involvement ensures the product meets expectations.
- Risk Management: Regular iterations allow for early identification and mitigation of issues.
- Fast Time to Market: Facilitates quicker product releases and adaptations.
Cons of the Agile Model
- Scope Creep: The flexibility can sometimes lead to an expanding project scope without clear boundaries.
- Resource Intensive: Often demands more time and resources for continuous management and iterations.
- Less Predictability: The lack of a defined end-point can make it challenging to estimate timelines and costs.
- Overkill: Might be overwhelming for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal changes.
Differences Between Waterfall And Agile
Choosing the correct project management approach can make a huge difference in your project's success. Here's a closer look at the main distinctions between the Waterfall and Agile approaches:
Approach: The waterfall takes a systematic, linear approach. Each stage of the project (planning, development, testing, and deployment) is completed sequentially before proceeding to the next. Agile, on the other hand, uses an iterative and incremental approach. The project is divided into smaller portions ("sprints"), with ongoing planning, development, testing, and feedback loops included.
Flexibility: Waterfall projects have minimal flexibility. Once a stage is done, adjustments are difficult and typically expensive to execute. Agile thrives on adaptability. Changes, even in later stages of development, are welcomed and implemented depending on ongoing input.
Project Planning: Waterfall requires substantial upfront planning. The entire project path is outlined in full from the start, with little possibility for change. Agile planning is less detailed. Initial plans are developed, but they are regularly updated and adjusted as the project continues depending on fresh information and feedback.
Customer involvement: Customer participation in Waterfall is significant during the initial requirements phase but decreases as the project continues. Agile encourages ongoing and extensive client participation throughout the project's lifespan. Customers actively participate in offering input and influencing the project's path.
Team Structure: Waterfall projects frequently involve isolated teams. Each project phase has its dedicated team (e.g., requirements team, development team, testing team) that works independently until their assigned task is completed. Agile encourages cross-functional and collaborative teams. Throughout the project, team members with varied skill sets collaborate to improve communication and problem-solving abilities.
Risk Management: Waterfall risk management involves identifying and managing potential hazards during the first planning stages. The goal is to address these risks before they jeopardize the project. Agile takes a more continuous approach to risk management. Risks are identified and addressed throughout the project lifecycle when they arise throughout the development and feedback phases.
Explore Further: Lean vs Agile
Which approach to choose?
The waterfall is ideal for projects with clear schedules and deliverables. If your primary project limitations are clearly understood and documented, Waterfall is probably the best strategy.
The agile technique was developed for projects with considerable restrictions that are not fully understood. If your project entails creating a new product, the scope and duration may be challenging to predict in advance. Agile is adaptable, allowing you to plan a project in stages or "sprints" that alter as work goes on.
Final words
When selecting a project management approach, it is critical to evaluate all elements, including the nature of the project, stakeholder needs, time-frame, and financial restrictions. Teams can increase their chances of success and produce high-quality products by carefully considering the project's requirements and selecting the approach that best meets those requirements. Contact Prioxis today to discuss software project management.
Contact Us Now to Get Started
01 Does Agile cost more than Waterfall?
Agile's iterative structure, which necessitates continual stakeholder input and frequent iterations, may appear more expensive at first.
02How can I determine if Agile or Waterfall is best for my project?
Consider Agile if your project has dynamic requirements, requires frequent customer feedback, and prioritizes adaptability. Waterfall is best suited for projects with well-defined criteria, limited client engagement throughout development, and a need for structure.
03How can hybrid project management bring together Waterfall and Agile?
Because Agile and waterfall both have substantial advantages, firms throughout the world are looking for ways to integrate them while minimizing their shortcomings. Hybrid project management combines Agile and Waterfall methodologies to provide a solution that maximizes time, resources, and user satisfaction.